Animation is a fascinating field that combines technical know-how and creative thinking. In your work with Cinema 4D, you will find that Timing and Spacing are fundamental to the quality of your animations. They are the building blocks of every moving graphic, and understanding these concepts will help you create more dynamic and realistic animations.
Key Insights
- Timing and Spacing are central principles of animation.
- Posing defines the positions of the objects, Timing determines the timing of these movements and Spacing defines the path in between.
- Conscious use of easing techniques, such as “Slow In” and “Slow Out,” enhances the perception of movements.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Understand the Basics of Animation in Cinema 4D
Start your project in Cinema 4D (current version or an older one). Make sure you are familiar with the user interface. It is important to navigate the software as many functions are timeless and can also be found in older versions.
2. Apply Timing Principles
Timing refers to when certain movements occur. The art of timing lies in finding the right moment to make movement realistic and appealing. First, learn to define the basic poses of your animations before dealing with the timing.
3. Posing: Establish Key Positions
Posing is the stable positions that your objects take during their animation. For example, you can create two keyframes: one at -100 cm and one at +100 cm. With this first step, you're setting the stop points of your objects.
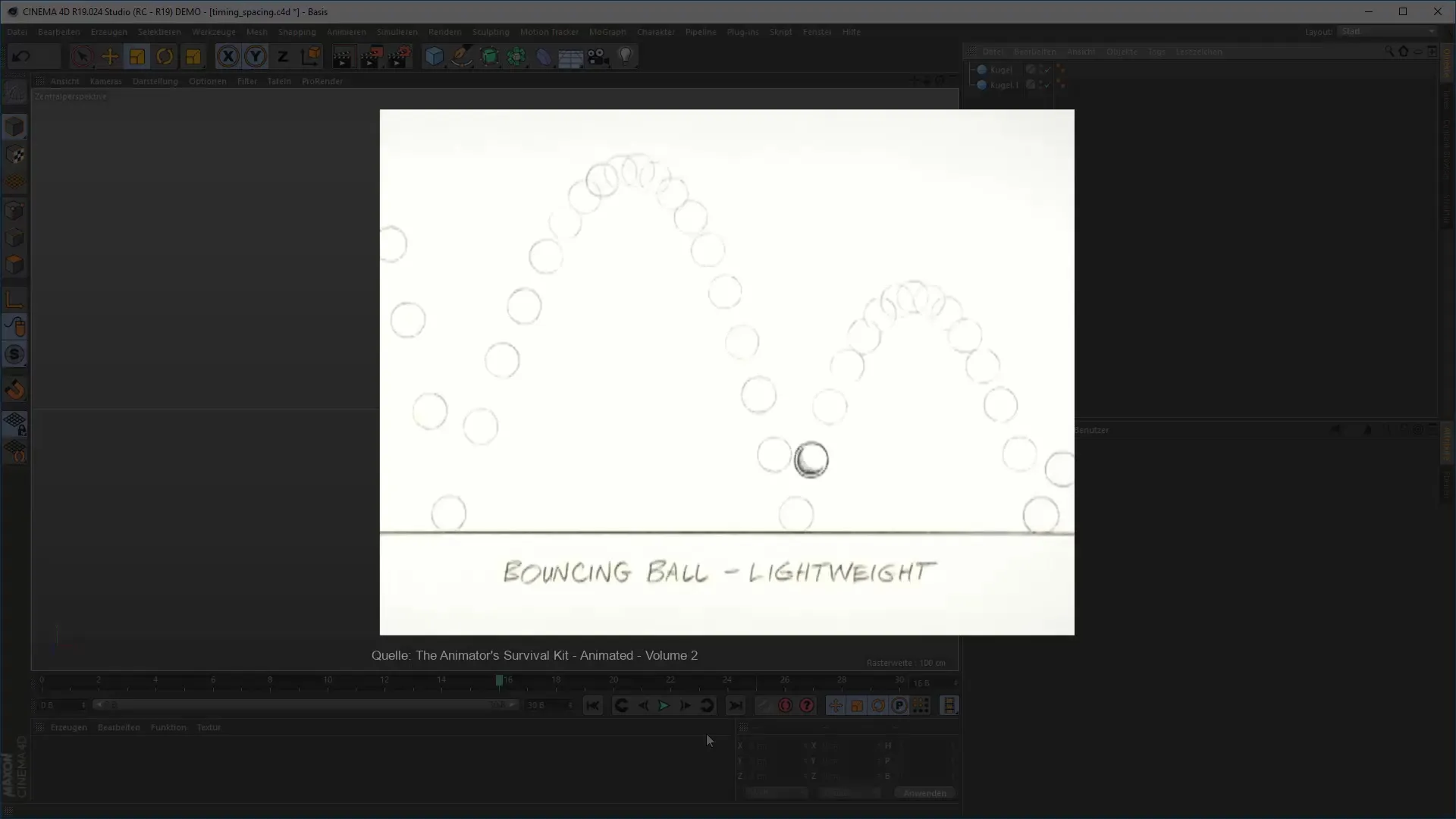
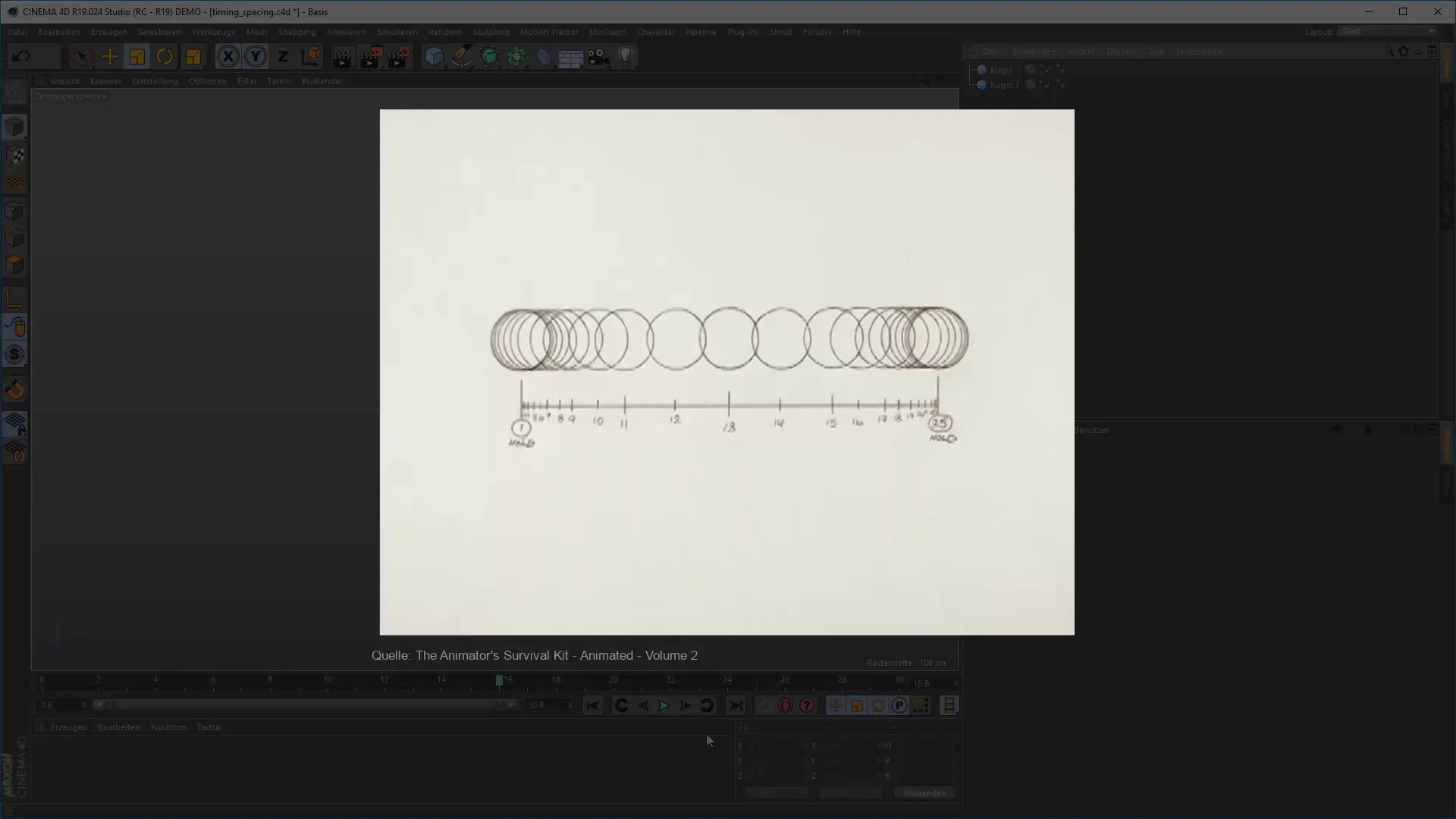
4. The Path Between Keyframes: Define Spacing
Spacing describes the gap that your objects cover between these keyframes. Pay attention to how the objects move as they transition from one keyframe to another. Here, you can experiment to decide whether the movement should be smooth or variable.
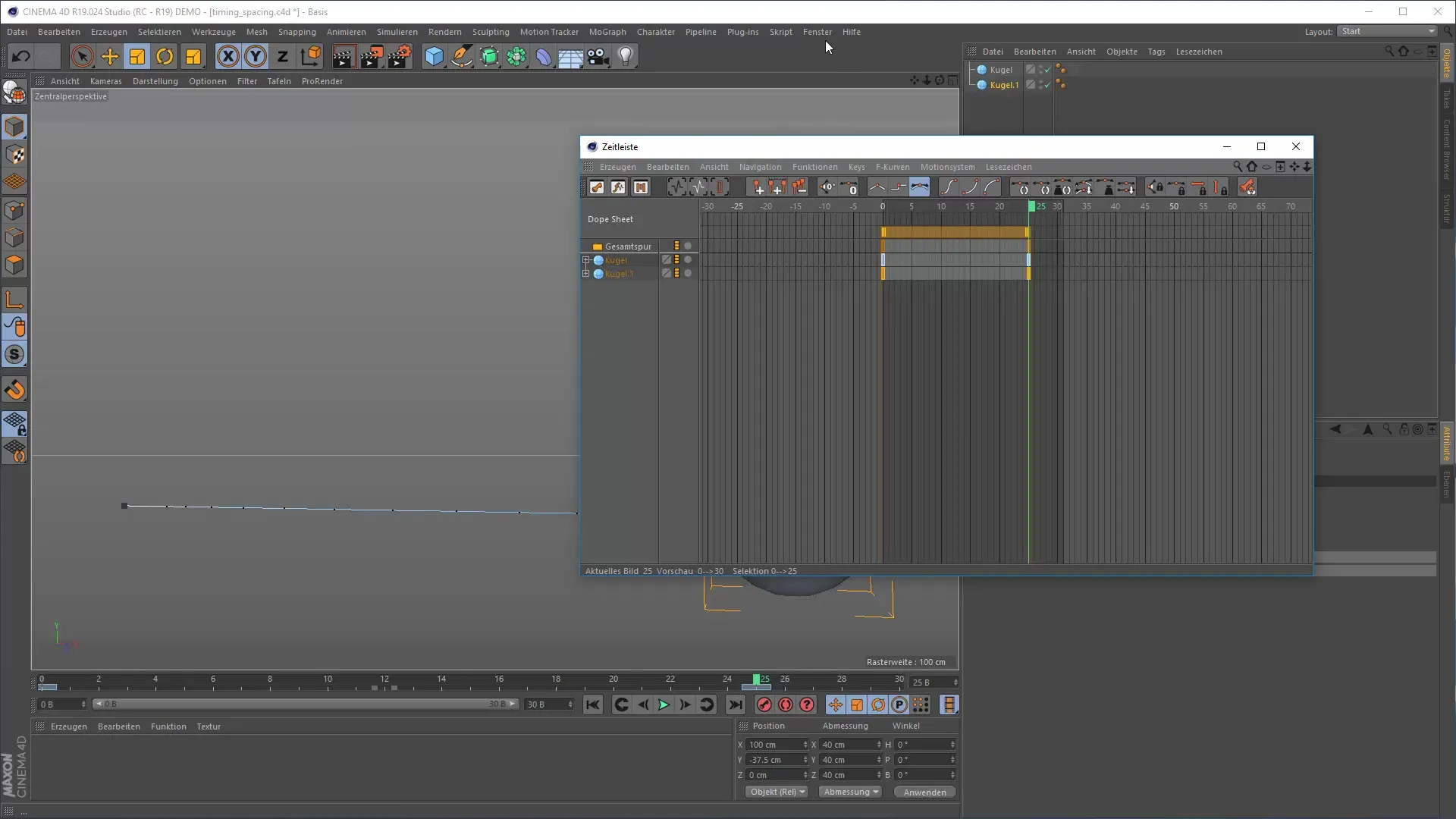
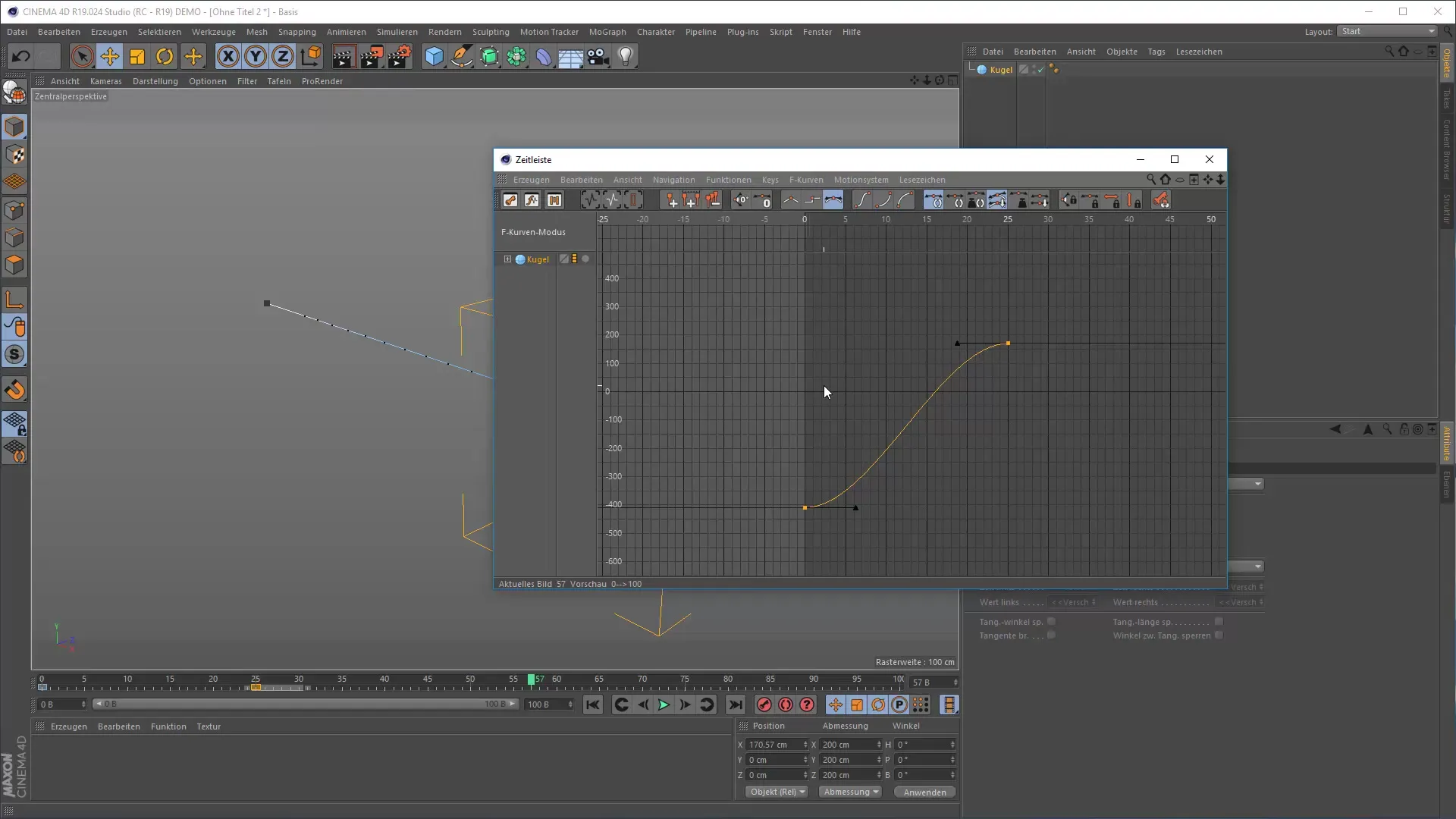
5. Working with the Timeline and F-Curves
Open the timeline in Cinema 4D. Here, you can manage your keyframes. To control the spacing precisely, switch to the F-Curve Editor. This allows you to adjust the acceleration and deceleration of your movements. A steep rise in the curve indicates fast movement, while a flat curve represents slow movements.
6. Easing Techniques: Slow In and Slow Out
Easing is a crucial aspect of creating movement realism. This means that the animation does not start or stop abruptly, but accelerates or decelerates smoothly. Use Slow In and Slow Out strategically to add depth to your animation.
7. Experimenting with Movements
To apply what you've learned, animate a simple object, such as a clock. Vary the timing and spacing to see how the perception of the animation changes. You can do this by adjusting the curve in the F-Curve Editor. Try different settings and observe the results.
8. Reflecting on the Results
Before finalizing your animation, review it and ask yourself: Is the movement dynamic? Does it convey the desired emotion? Make any necessary adjustments based on your knowledge of timing and spacing.
Summary – 3D Animation in Cinema 4D: Understanding Timing and Spacing
In the world of 3D animation, especially in Cinema 4D, understanding timing, spacing, and posing is essential for producing high-quality outcomes. By consciously designing these elements, you can create livelier and more engaging animations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are timing and spacing important?They are the foundations of every animation that ensure realistic feeling of movements.
How do easing techniques affect the animation?They create smoother transitions and make the movement more believable.
What are F-Curves in Cinema 4D?F-Curves are graphical representations of your animation that visualize speed and acceleration.
Can I apply these principles in other animation programs?Yes, the principles of timing and spacing are universal and applicable in most animation software.
How can I optimize the timing of my animation?By setting precise keyframes and experimenting with the timeline and F-Curves, you can optimize the timing.


