If you want to become self-employed as a freelancer on the web, there are numerous legal aspects to consider. A wrong decision or a missed point can quickly lead to warnings or unwanted costs. Therefore, it is crucial to thoroughly inform yourself about the legal requirements and avoid some specific pitfalls. Here you will find a step-by-step guide to master the most common legal challenges.
Key Insights
- Mandatory information such as the imprint is essential.
- Copyrights must be observed, especially when using media and images.
- Privacy policies must be created and published.
- Trademark rights must not be infringed upon.
- There are numerous specific regulations, especially in e-commerce.
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Create an Imprint
Your website needs a legally secure imprint. The provider identification is legally required in Germany. Without a correct imprint, you can quickly fall into the warning trap. Use an imprint generator to provide all mandatory information. You must ensure that it is easily accessible - for example, in the footer of your website.
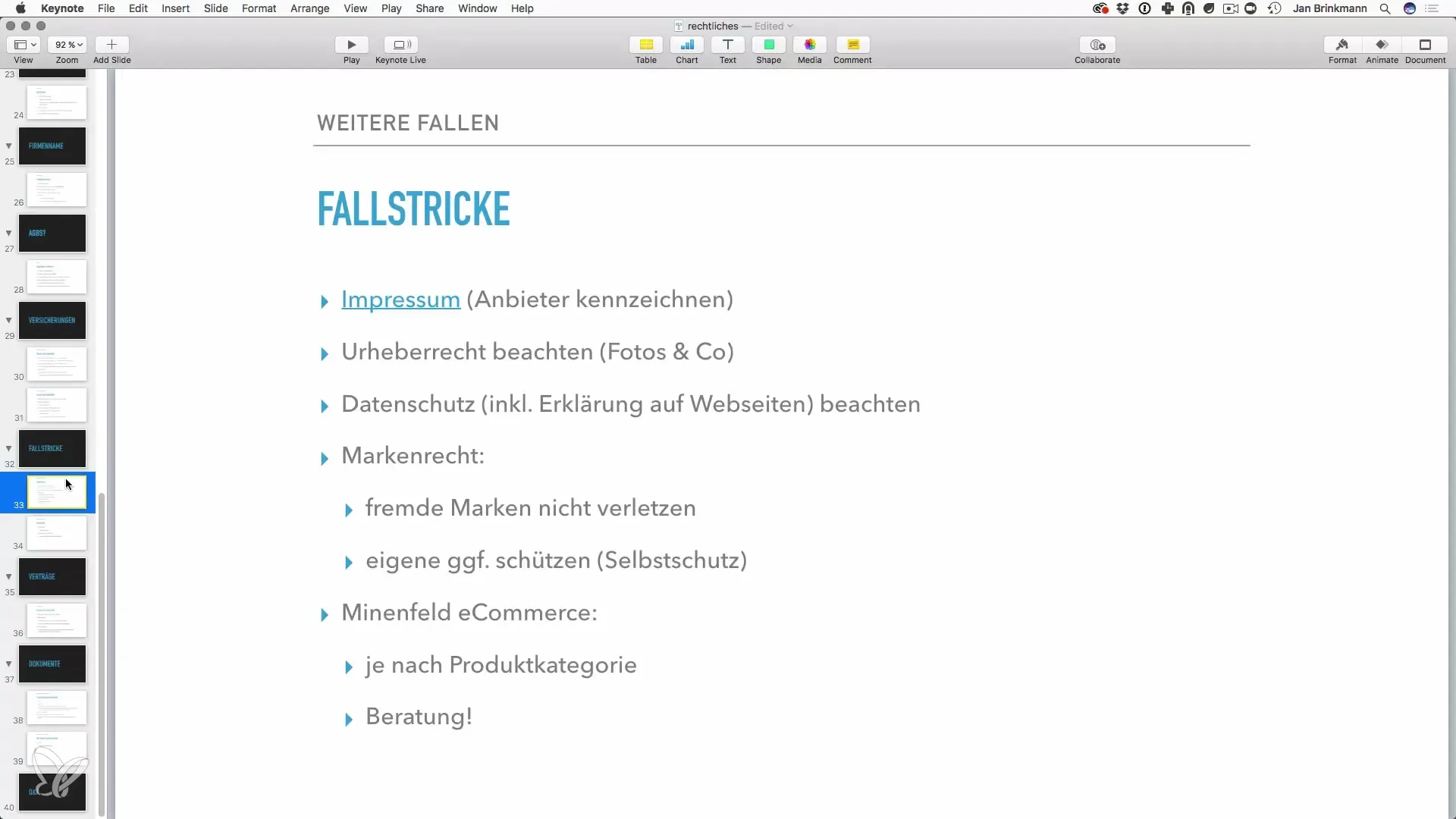
Step 2: Keep Copyright in Mind
Make sure that you observe copyright laws when inserting media content such as images or videos. Check if the files are royalty-free or if you have permission to use them. There are different types of licenses that regulate the use of images: some allow commercial use, others do not. It's better to inform yourself about the licensing terms beforehand.
Step 3: Implement the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Whether you use a newsletter form or Google Analytics, you need to inform yourself about the General Data Protection Regulation. Make sure to create a separate page with a privacy policy and make it accessible via a link in the imprint. Use generators to create the content for the privacy policy as well.
Step 4: Consider Trademark Aspects
Remember that you may not use third-party trademarks in your content or domain name. For example, you may not use the term "iPhone" in your AdWords campaigns, as this violates trademark law and may lead to a domain seizure. Also, consider whether you want to register your own trademark to protect your name.
Step 5: Observe E-commerce Specific Laws
If you want to sell products online, you need to consider various legal provisions that may vary depending on the product category. In particular, the fixed book price law also applies to eBooks. Inform yourself about the regulations that apply to your products. Handling batteries requires additional knowledge and can become complicated.
Step 6: Use the Double Opt-In Procedure
If you send out newsletters, the double opt-in procedure is necessary. This is a legally secure way to ensure that your subscribers consent to receive the newsletter.
Step 7: Legally Integrate Analytics
If you want to use Google Analytics or similar tools, ensure that the integration complies with European data protection regulations. This can be complicated, as many regulations need to be considered. Inform yourself thoroughly to avoid legal pitfalls.
Summary – Start-up: Avoiding Pitfalls for Freelancers on the Web
In summary, as a freelancer, you must consider a variety of legal pitfalls on the internet. From imprint to copyright to data protection and trademark law, there are many aspects that you should thoroughly examine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an imprint and why is it important?An imprint is a legal mandatory information on your website that provides information about the operator. Without an imprint, you risk warnings.
How do you protect your own content?You should educate yourself about the use of media and observe copyright laws. If necessary, you can register your own trademarks.
What must be included in a privacy policy?A privacy policy informs users about the data usage on your website and is legally required.
What is the double opt-in procedure?The double opt-in procedure ensures that users explicitly consent to receive newsletters.
How do e-commerce regulations deal with fixed book prices?The fixed book price law stipulates that electronic books may not be offered at different prices on different platforms.


