The spread-operator is a versatile tool in JavaScript that allows you to handle objects and arrays efficiently. You will learn how to merge objects using the spread operator and what alternatives exist. Let's dive right in!
Key insights
- The spread operator can be used to combine multiple objects into a new object.
- Object.assign() is a flexible method that yields similar results as the spread operator but may allow for other use cases.
- Both methods only copy the first level of the objects; nested objects remain referenced.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Spread Operator with Objects
Let's start with a basic understanding of the spread operator in JavaScript, specifically for objects.
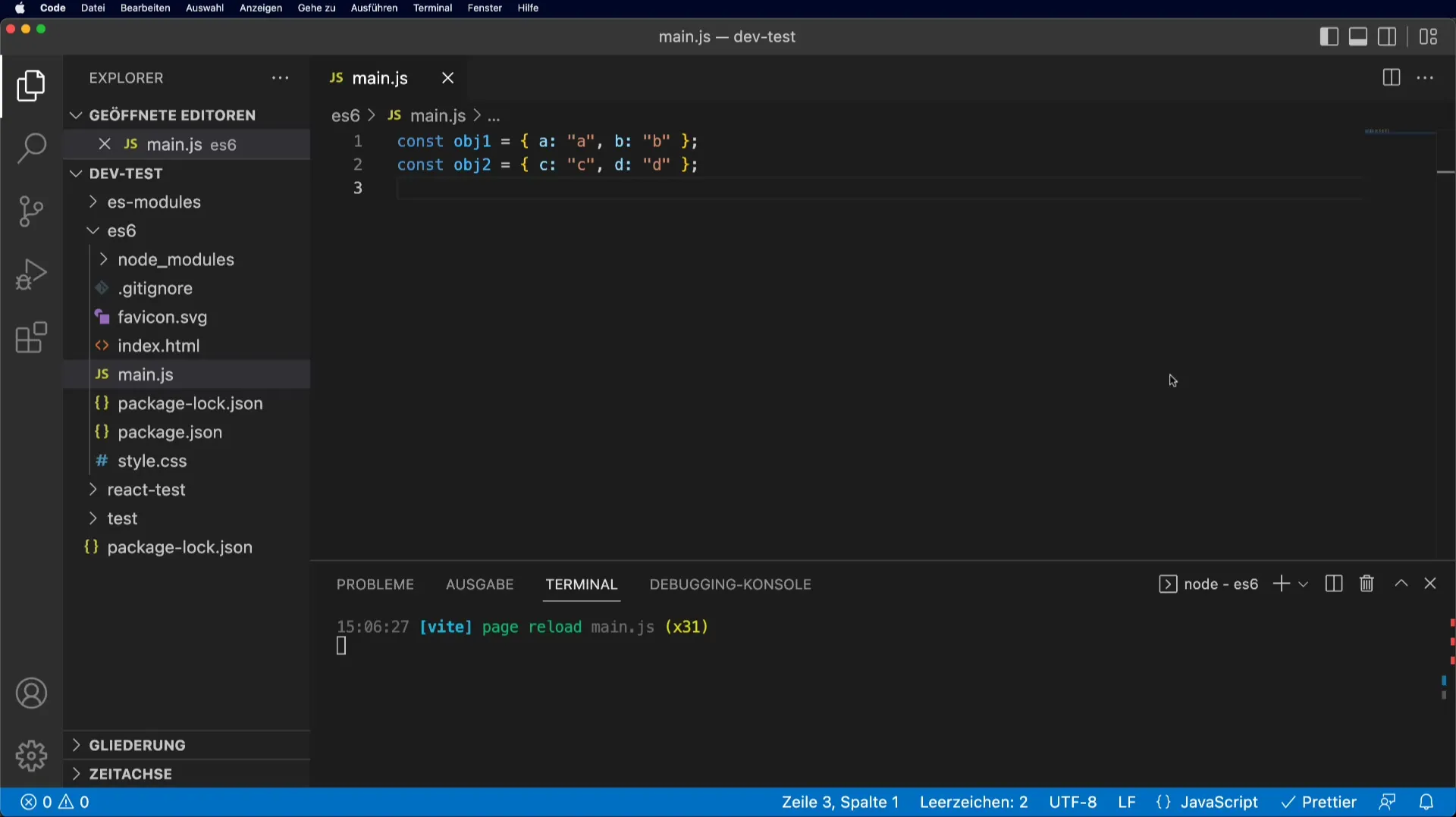
Step 1: Create Objects
To work with the spread operator, you first need to define some objects. Let's assume you have two objects, obj1 and obj2.
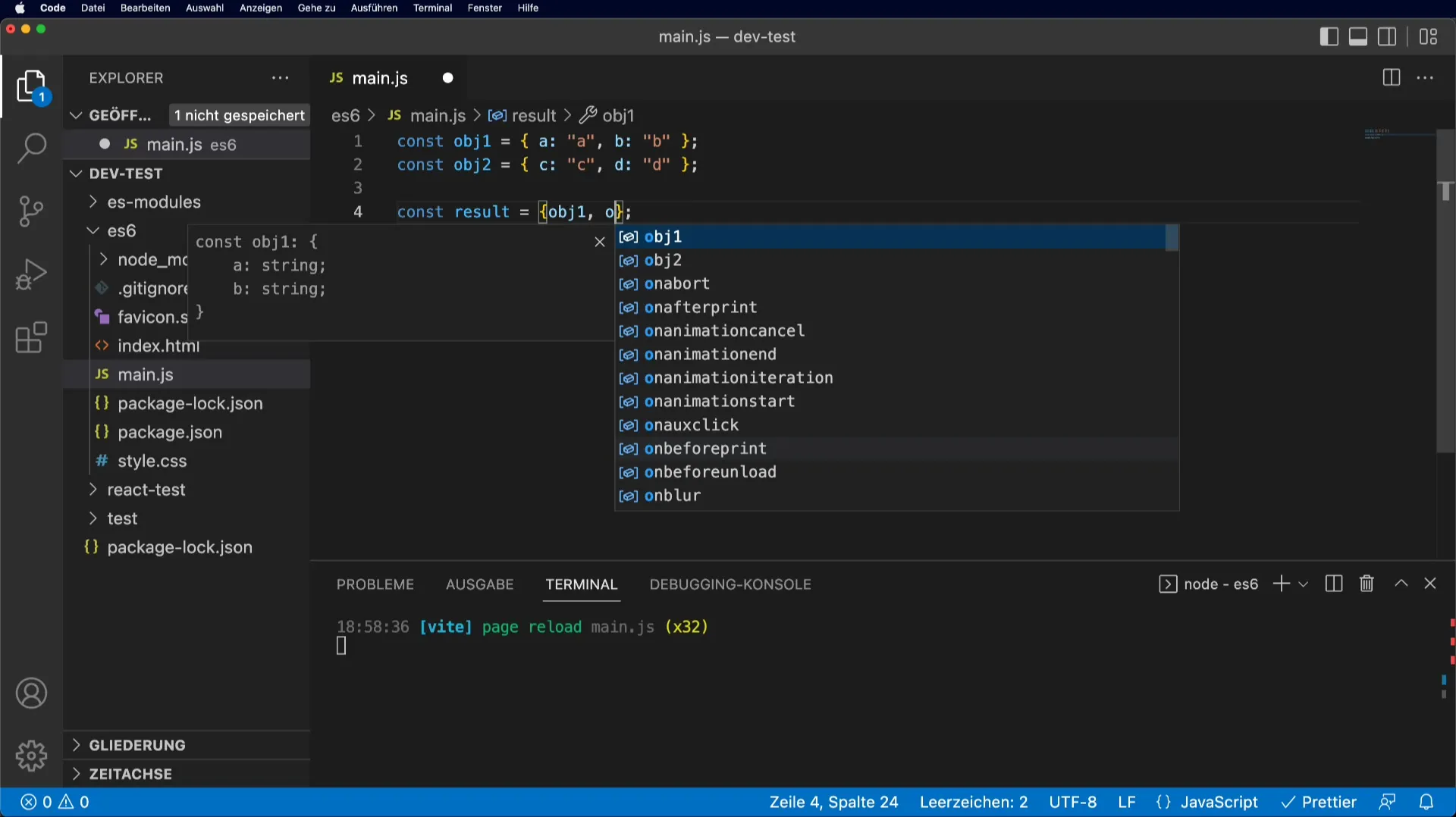
Step 2: Applying the Spread Operator
Now you want to merge both objects into a new object called result. To do this, you place the spread operator (...) before the objects.
Here, result will contain all the properties from obj1 and obj2.
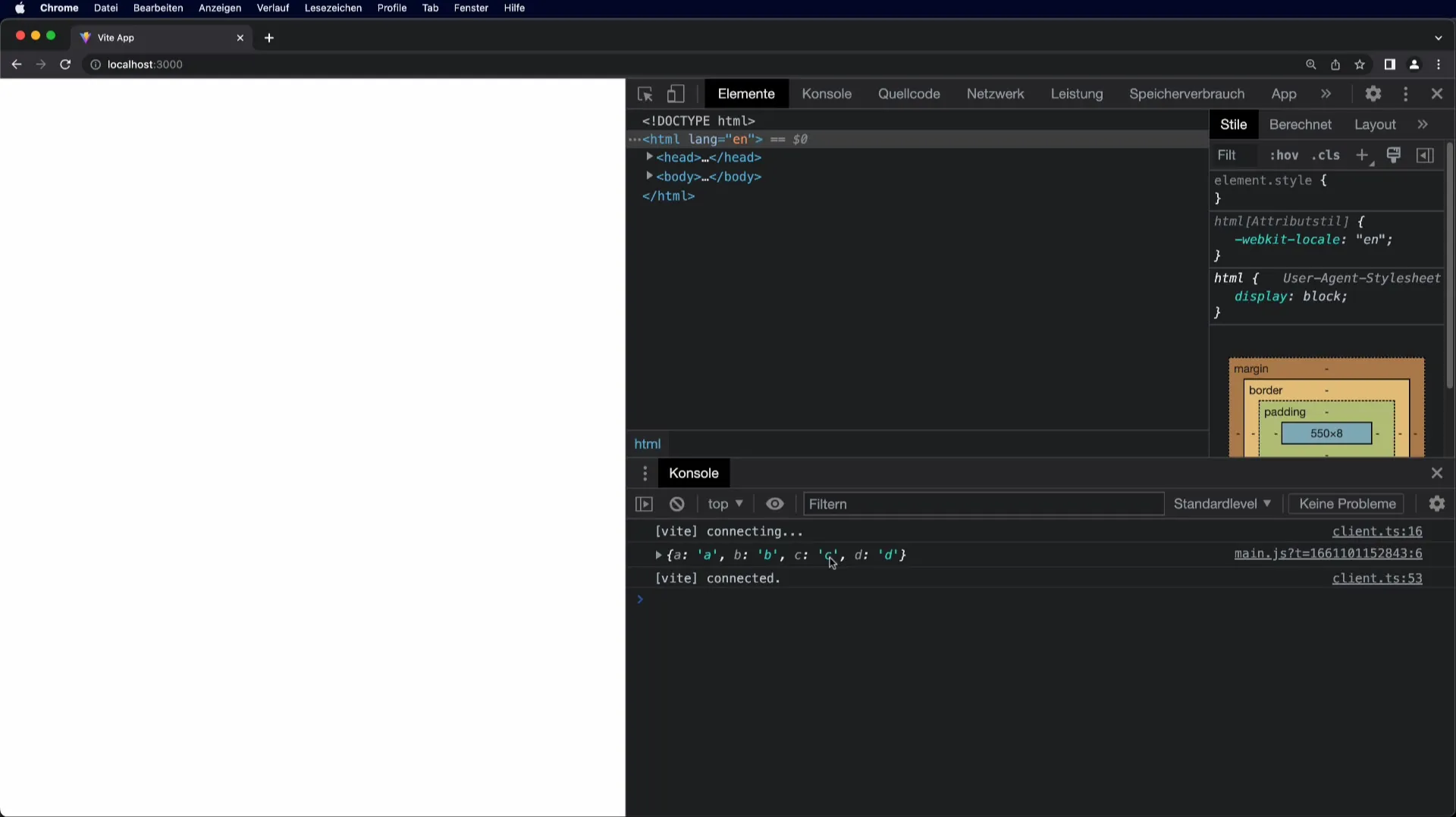
Step 3: Check Results
To check if the objects have been merged correctly, you can use the console.
Step 4: Adding Properties
Additionally, you can add more properties to the new object.
Step 5: Order of Properties
The order of properties in the resulting object is based on the order in which you specify the objects and properties in the code. Here, the property f will appear after obj1 and obj2.
Step 6: Using Object.assign()
An alternative to the spread operator is the method Object.assign(). It works similarly but uses a different syntax. Here, you create an empty object as the target object and then add the properties from obj1 and obj2.
Step 7: Checking the Output
Similar to before, you can check the output of Object.assign().
Step 8: Combining Multiple Objects
You can also combine more than two objects by simply passing them as additional parameters to Object.assign().
Step 9: Omitting the Empty Object
If you omit the empty target object, obj1 will be overwritten and the properties from obj2 will be merged into obj1. Note that this modifies the original obj1.
Step 10: Conclusion on Deep Copy
It is important to know that both the spread operator and Object.assign() do not create deep copies of objects. They only copy the first level of properties. For more complex data structures, you may need to use other methods.
Summary – The Spread Operator for Objects: A Comprehensive Guide
In this guide, you have received a comprehensive introduction to the spread operator and the Object.assign() method. You learned how to merge objects and add new properties, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of both methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the spread operator work with objects?The spread operator copies the properties of an object into a new object.
Can I combine multiple objects with Object.assign()?Yes, you can combine an arbitrary number of objects with Object.assign() by passing them as parameters.
What happens if I pass an empty object to Object.assign() as the target?The empty object will be filled with the properties of the subsequent objects without altering the original target object.
Is a deep copy of objects created?No, both the spread operator and Object.assign() only create shallow copies of the objects.
Can the order of properties in the resulting object be influenced?Yes, the order of properties corresponds to the order in which you specify the objects.


