InDesign is a comprehensive tool for designing and laying out printed materials, and it has its own file format. Whether you start a new project or open an existing document, understanding the different file formats is essential. This guide will show you the basic file formats and how to effectively package projects to ensure that all necessary files are passed on to your colleagues or clients.
Key Insights
InDesign primarily saves in.indd files, which are not backward compatible. IDML files are backward compatible and ideal for collaborating with older versions of InDesign. The INDT format serves as a template that cannot be overwritten. Packaging files ensures that all linked elements and fonts can be sent in an organized package to others.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. The Default Format for InDesign:.indd
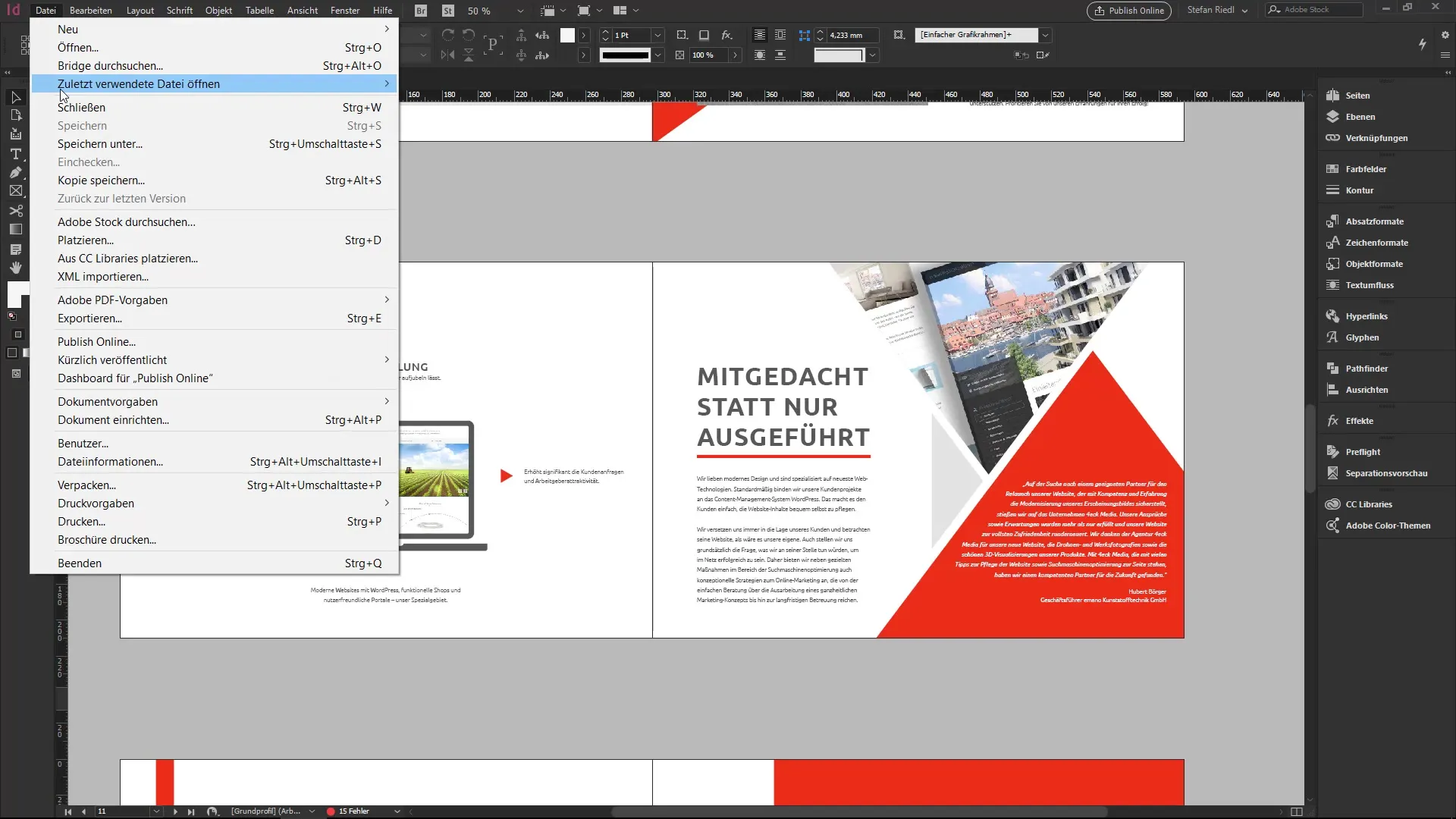
To get started with InDesign, you can open any document or create a new one. Now go to the "File" menu and select "Save As."
In the Save As dialog, you have the option to select the file type. The default format for InDesign is the.indd file, which can be opened on both Mac and Windows.
It is important to note that the.indd file can only be opened with the same or a newer version of InDesign.
2. Backward Compatibility with IDML
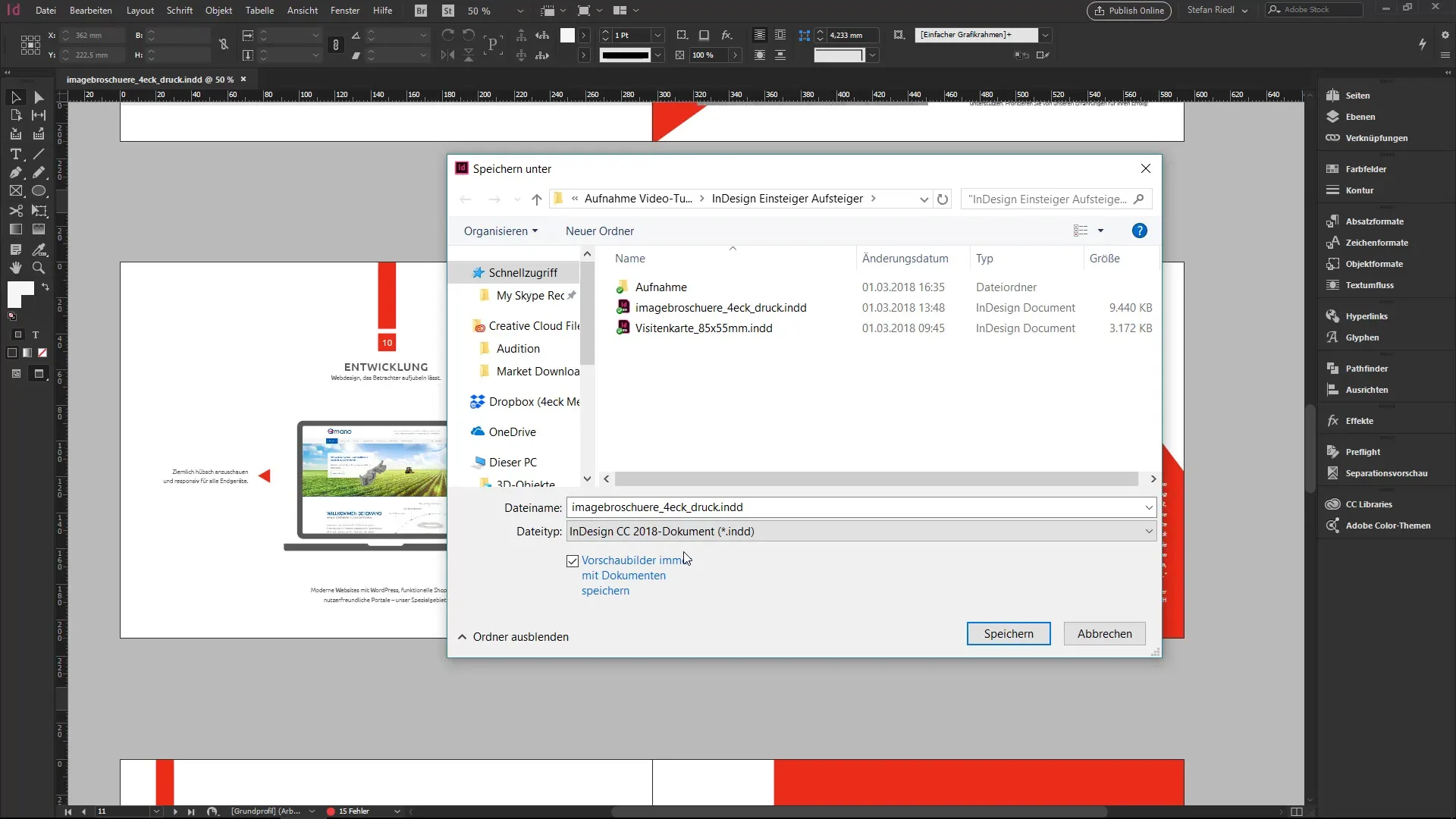
If you are working with a newer version of InDesign and your colleague is using an older version, you can save your.indd file as an IDML file. An IDML file is backward compatible, meaning it can be opened in older InDesign versions like CS6 or CS5.
To do this, go back to "Save As" and select the format "IDML." This ensures that your colleague can open the document without any issues.
3. Using the Template Format INDT
Another important format in InDesign is the INDT format, which allows you to create templates that cannot be overwritten. This is particularly useful for recurring documents, such as letterheads or questionnaires.
When you open an INDT file, InDesign will prompt you to give a new file name when saving.
4. Packaging Files
Once you have completed a project and want to pass it on to a colleague, you can use the "Package" function. This ensures that all necessary elements like images and fonts are included in a single package.
To package a document, go to "File" and select "Package." This opens a dialog where you can make various settings.
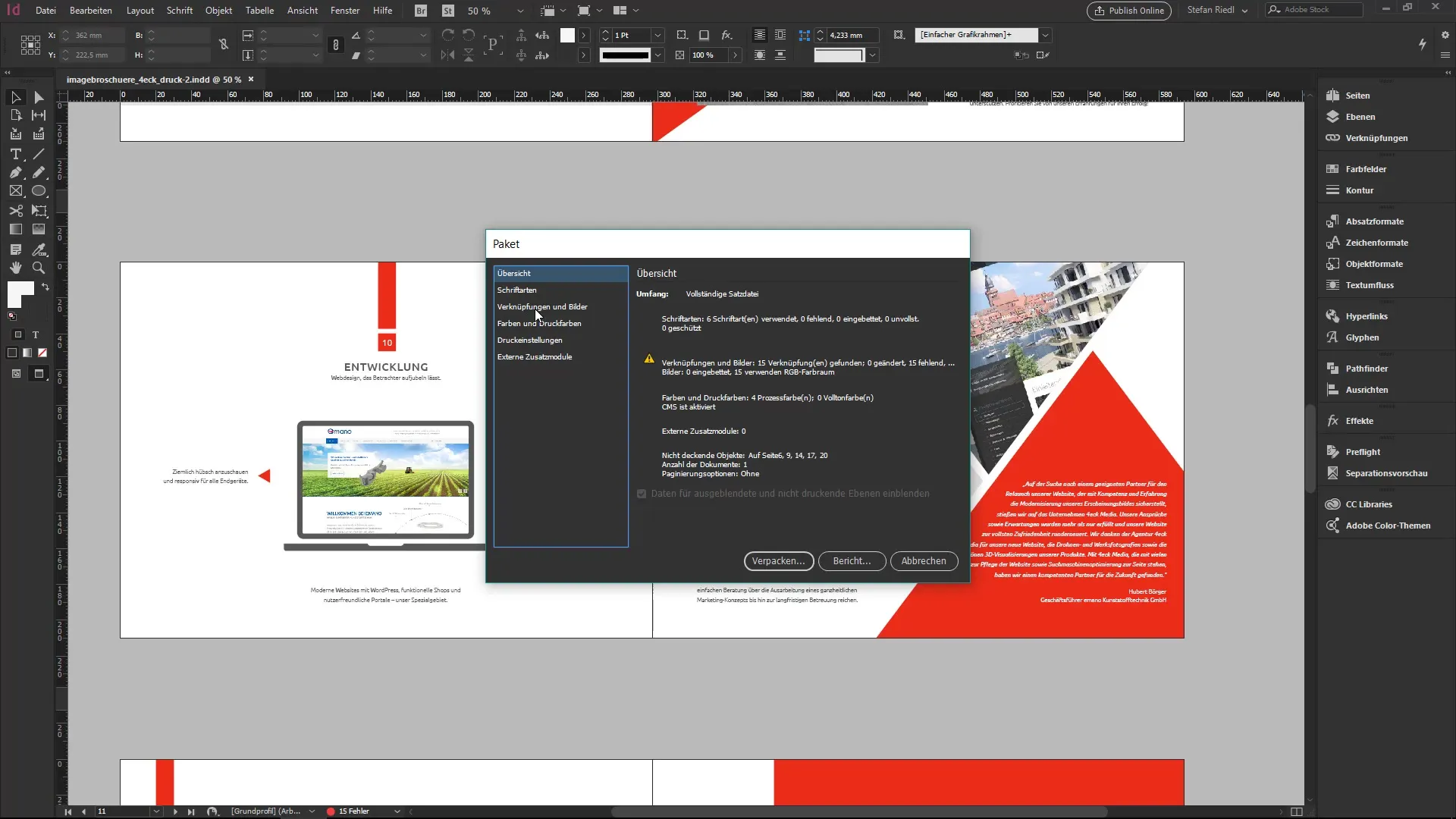
Note that there may be some warnings when packaging fonts, as they are often licensed. You can confirm the warning, but always be aware of the legal framework.
After confirmation, the document will be packaged and can be handed over to your colleague. You will then receive a package that contains all the necessary files for the work.
5. The Final Result
Finally, you can check the destination folder to see what you have packaged. You should find the fonts used, the IDML file, the.indd file, and even a PDF file.
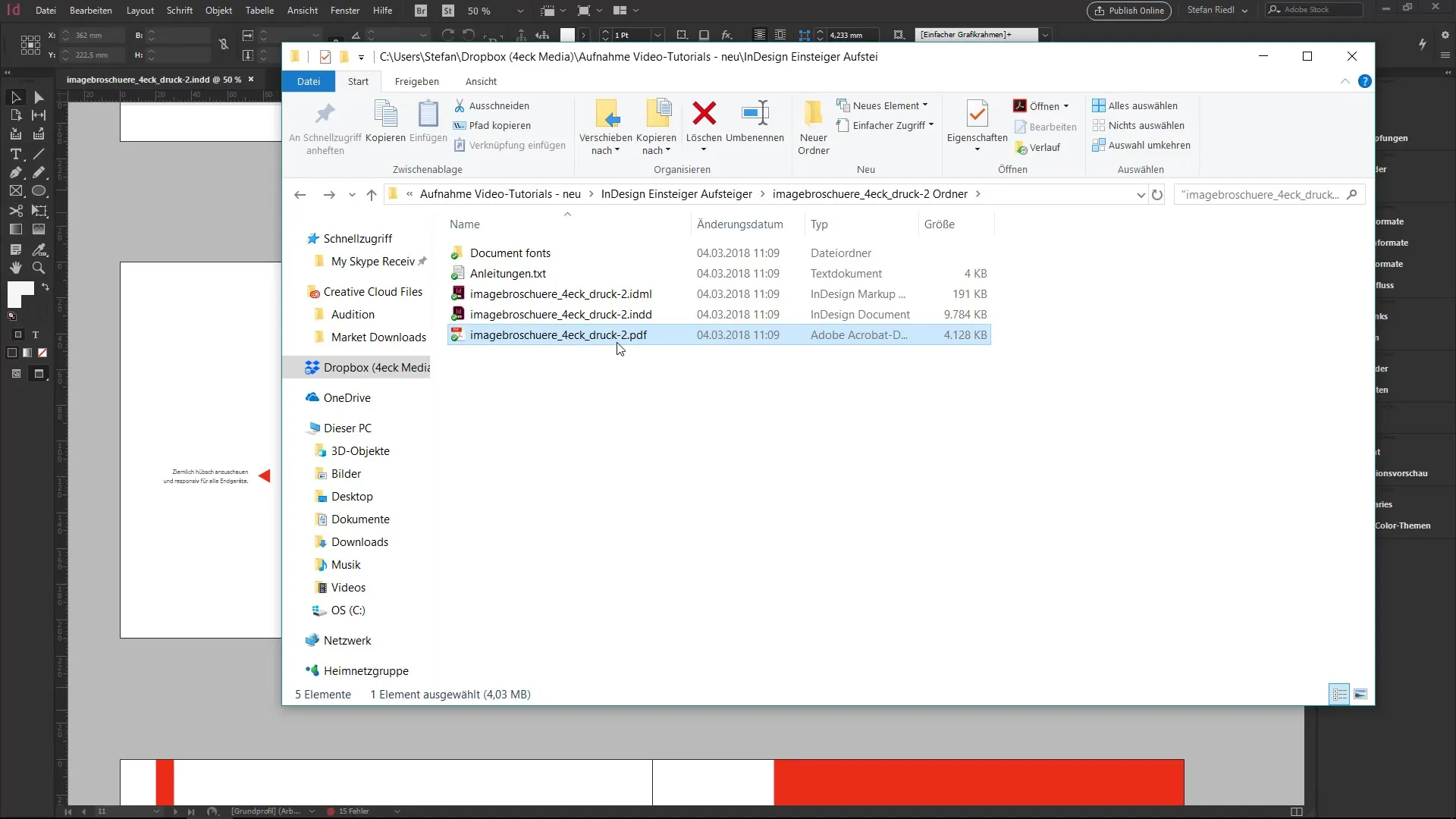
By using these different file formats and the packaging function of InDesign, you can effectively ensure that your projects are delivered in a clean and complete state.
Summary - InDesign: File Formats and Project Packaging Made Easy
Understanding the different file formats in InDesign as well as packaging files is essential for every user. This knowledge helps to optimize collaboration.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I save an InDesign document as IDML?To save an InDesign document as IDML, go to "File" > "Save As" and select the IDML format.
What is the advantage of an INDT file?An INDT file is a template that requires a new name upon opening, thus it cannot be accidentally overwritten.
What happens when I package a document?A packaged document contains all linked files, images, and fonts, allowing your colleague to work with it without restrictions.
What formats are available by default in InDesign?The default formats in InDesign are.indd, IDML, and INDT.


