Working with Linux can be challenging, especially when you need an overview of the running processes and their consumption of system resources. In this guide, I will show you how to effectively find out which programs are running and how to terminate them if necessary using the commands ps, top, and kill. This is particularly important when a process is affecting the performance of your system.
Key Insights
- With the command ps you can view all running processes.
- The command top provides a dynamic overview of system resources and their usage.
- With kill you can specifically terminate processes, thereby improving the stability of your system.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Display Processes with ps
To get an overview of currently running processes, use the command ps. This shows you the processes that are running under your user. The basic format is ps.
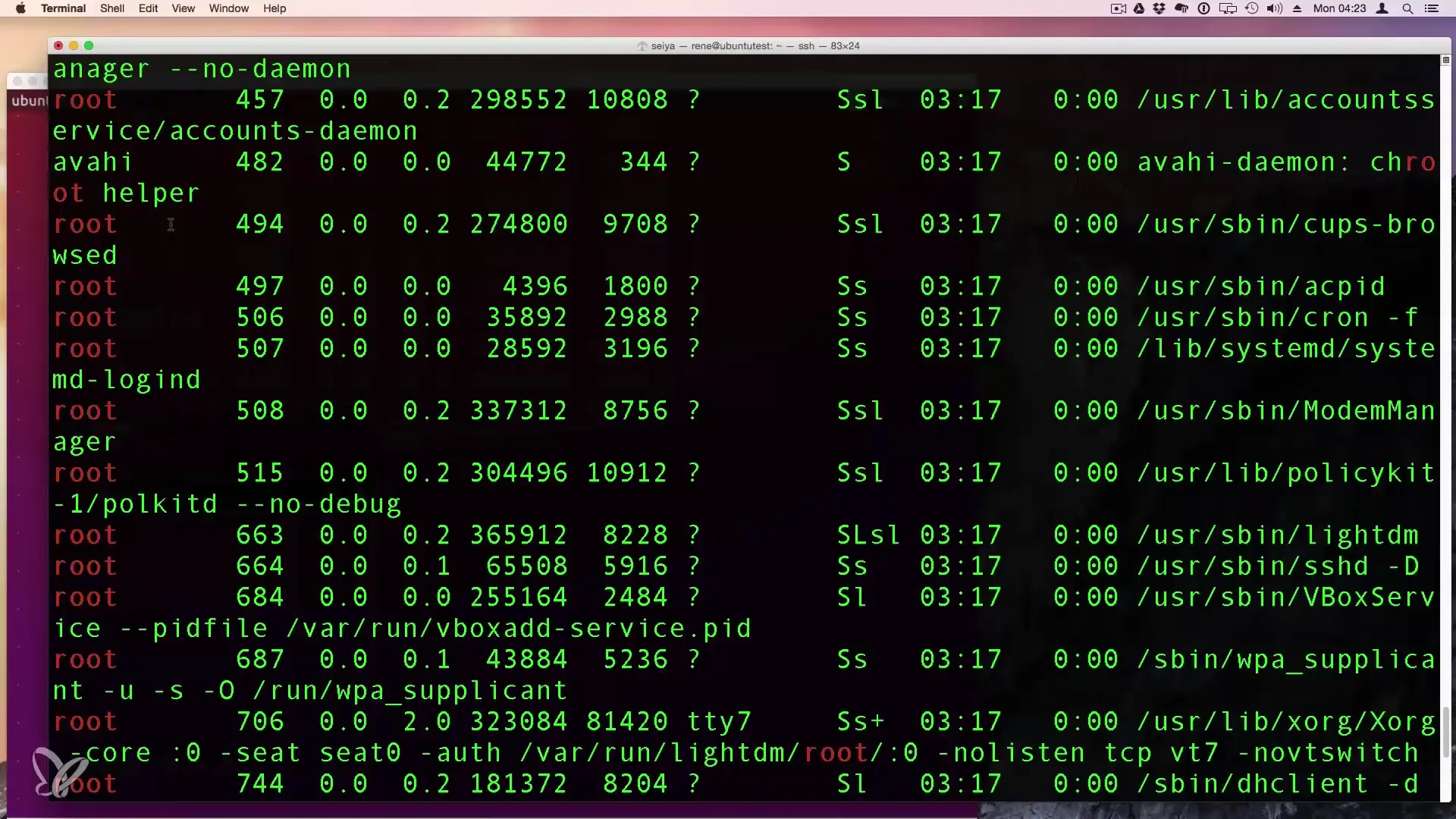
If you want to see all processes running on the system, you can specify the command ps -ax. This provides a more comprehensive list of processes, including those of the root user and other users.
2. Filter Specific Processes
If you are only interested in specific processes, you can use the command ps -ax | grep
3. Detailed Process Information with ps aux
For even more detailed information, you can use the command ps aux. Here you get a lot of information, including the PID (Process ID), CPU and Memory usage of each active instance.
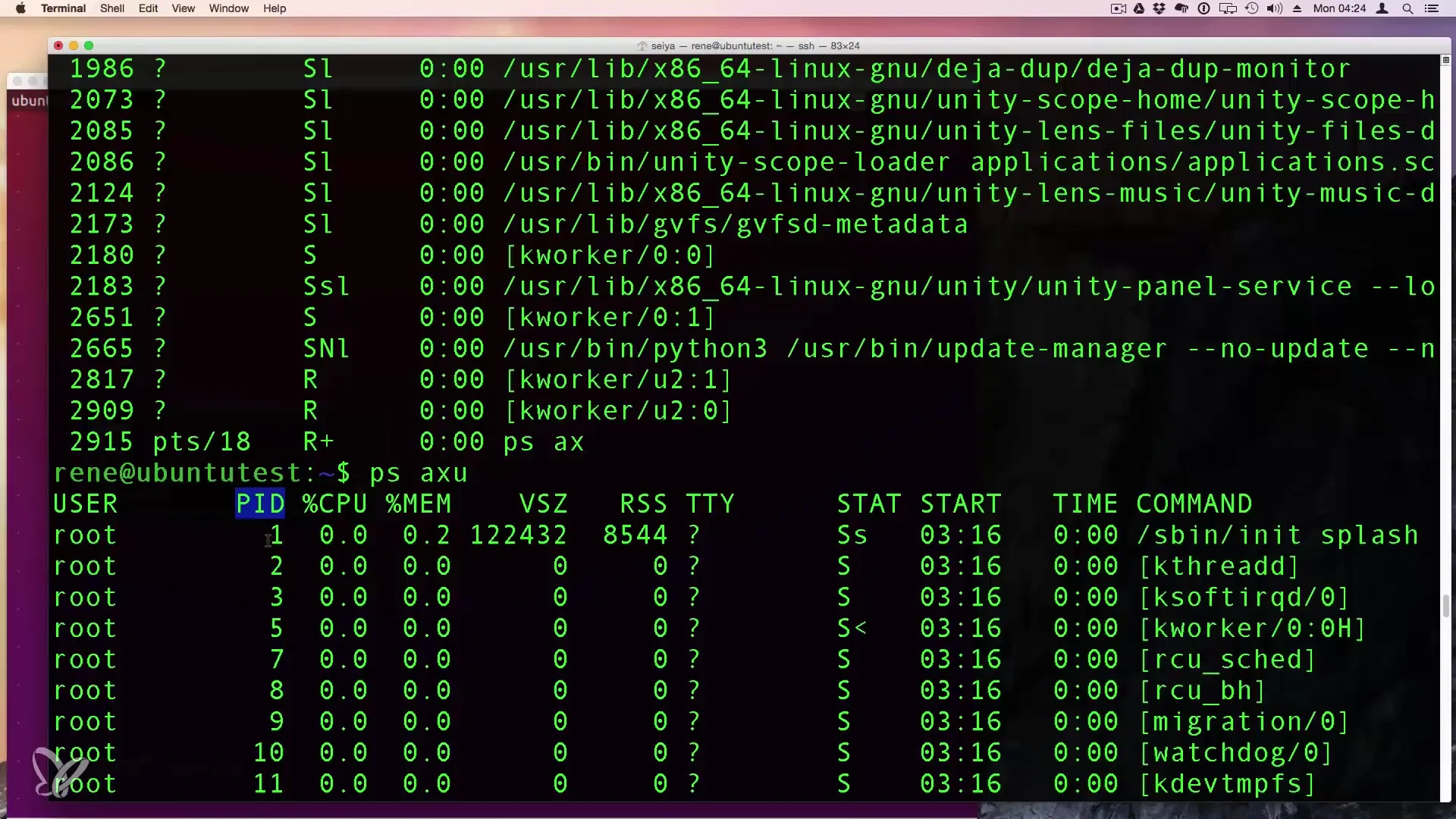
The most important aspect is the PID, which allows you to identify the specific processes.
4. Dynamic Overview with top
The command top gives you a dynamic list of processes that updates every two to three seconds. Just type top in your terminal, and you will get an immediate overview of the processes and their resource consumption.
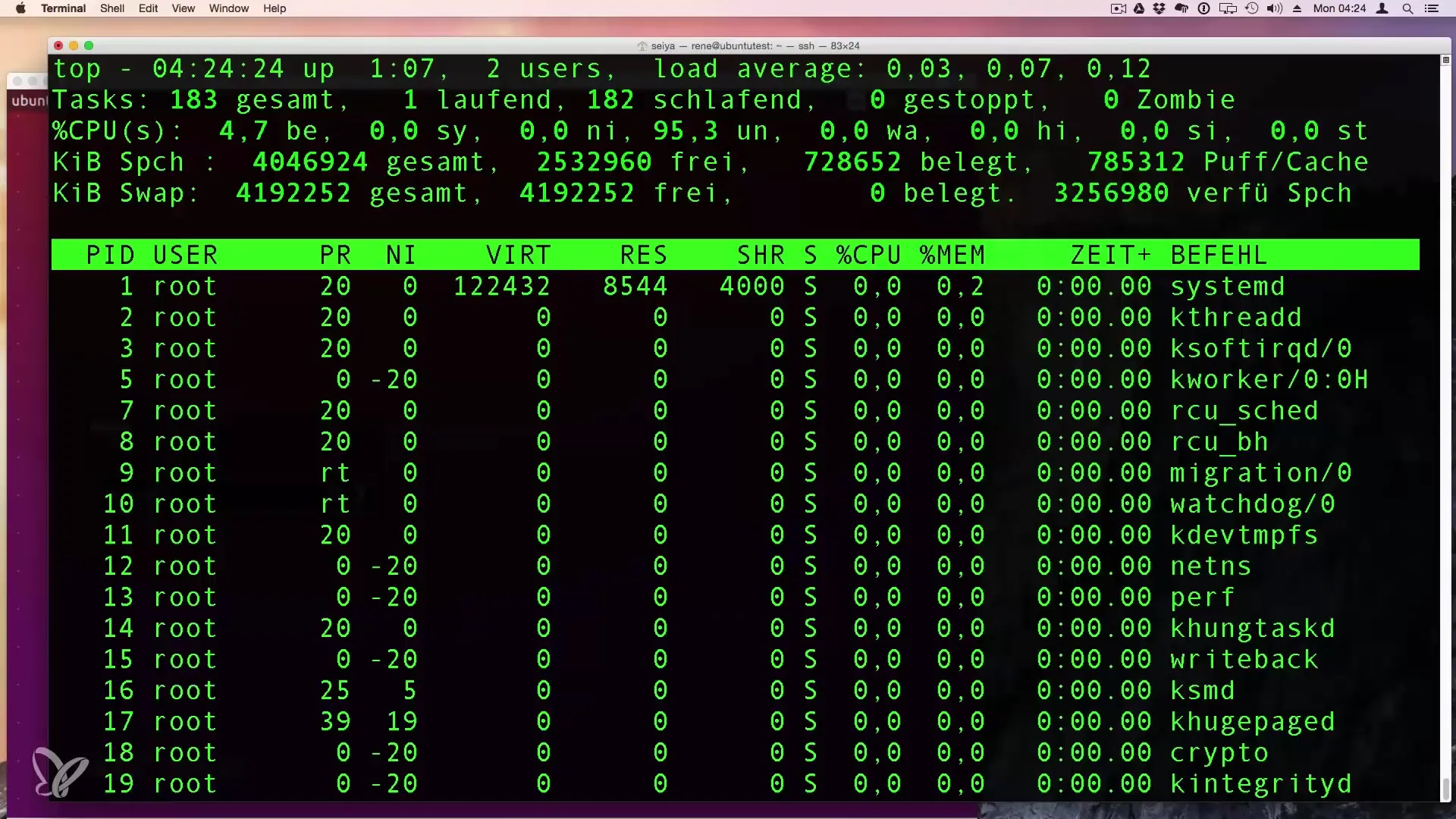
5. Sorting and Different Views in top
In the top view, you can adjust the perspective. Press the M key to sort the processes by their memory consumption.
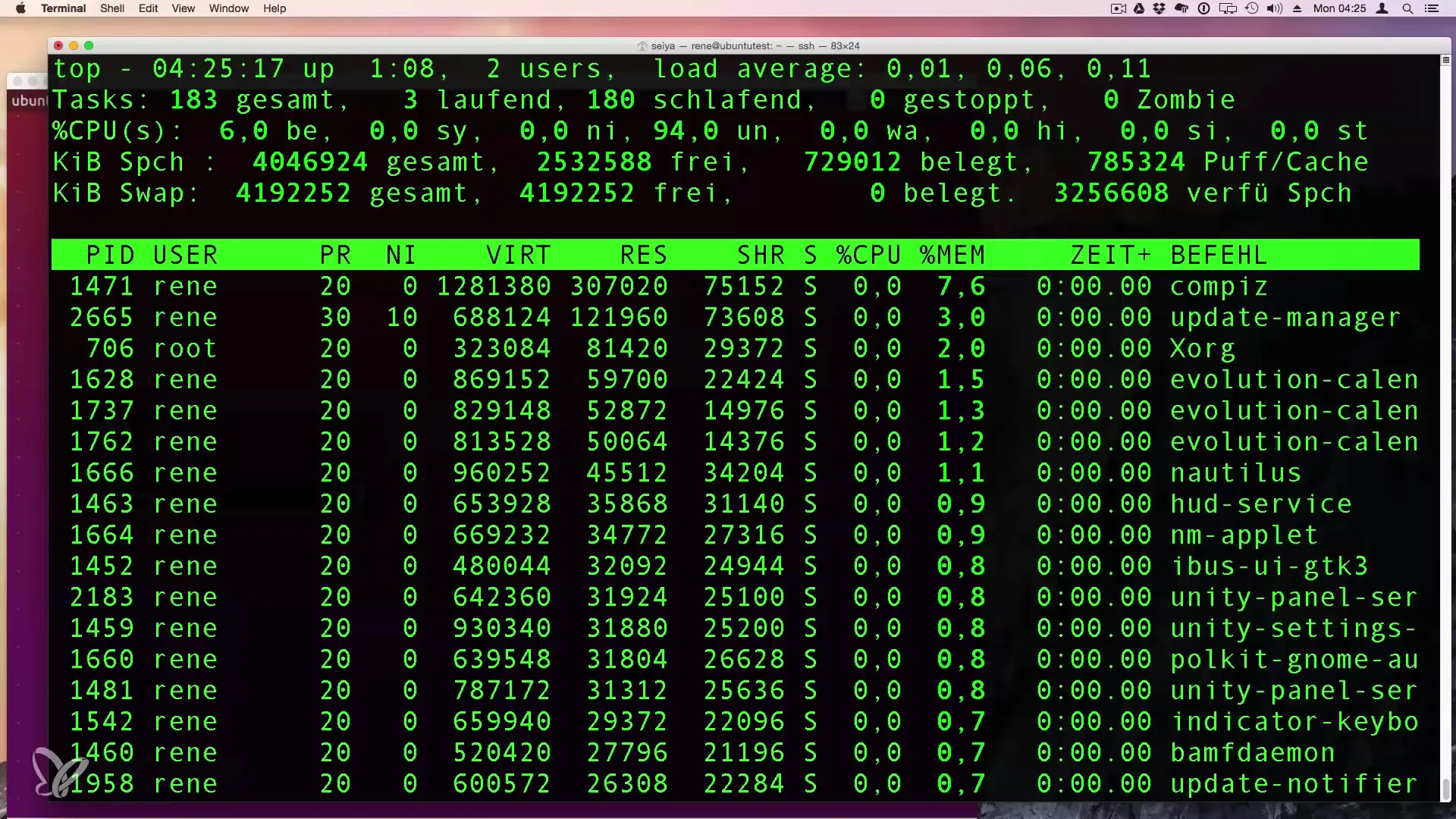
Clearly highlight the information by emphasizing the related columns.
6. Terminate Processes Directly from top
If you want to terminate a process while running the top command, press k (for kill) and enter the PID of the process you want to terminate. This allows you to kill the process directly.
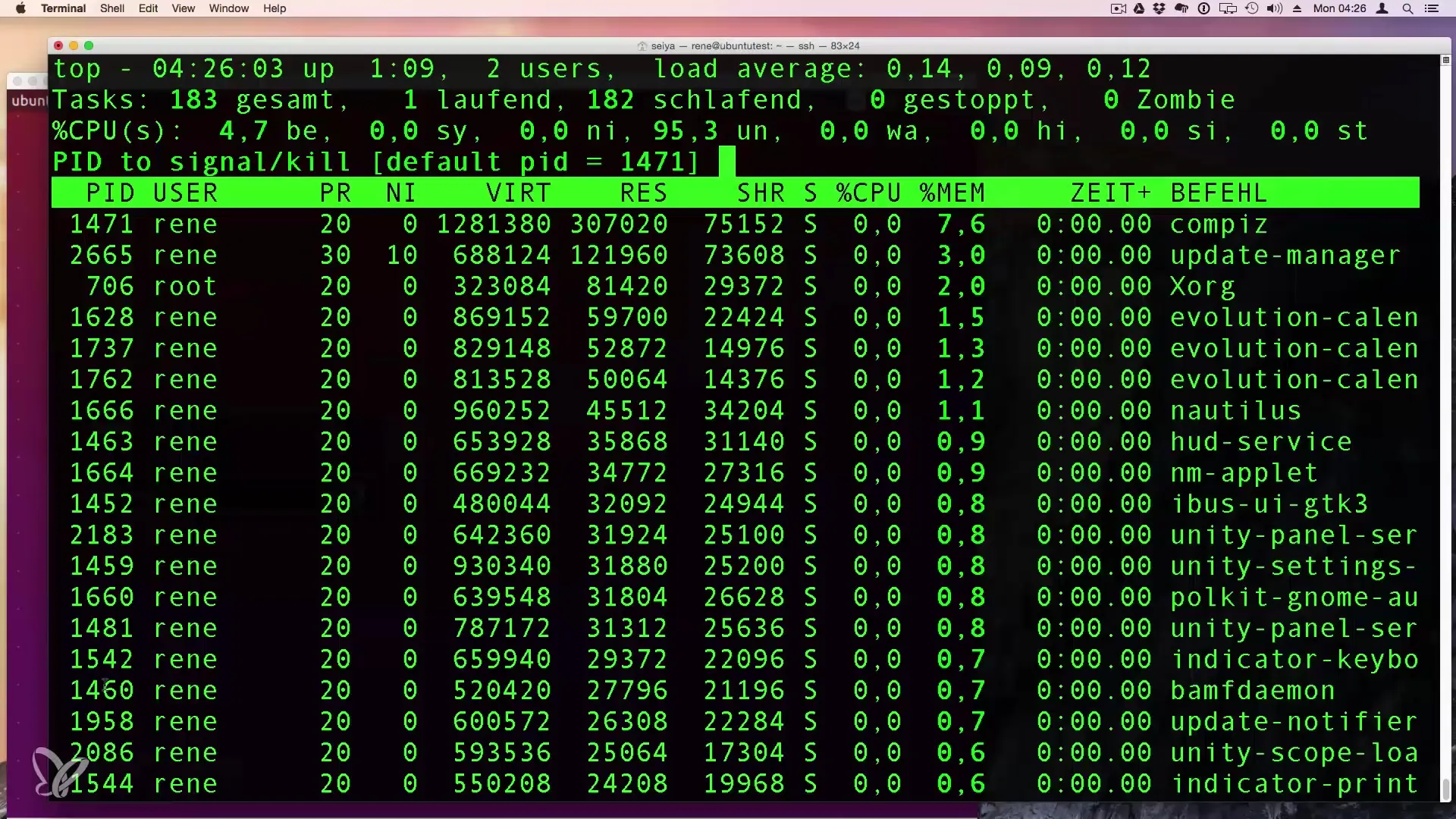
You can also check the PID on the list that is currently using the most memory.
7. Terminating Processes with kill
To terminate a process, use the kill command followed by the PID. For example, kill -9
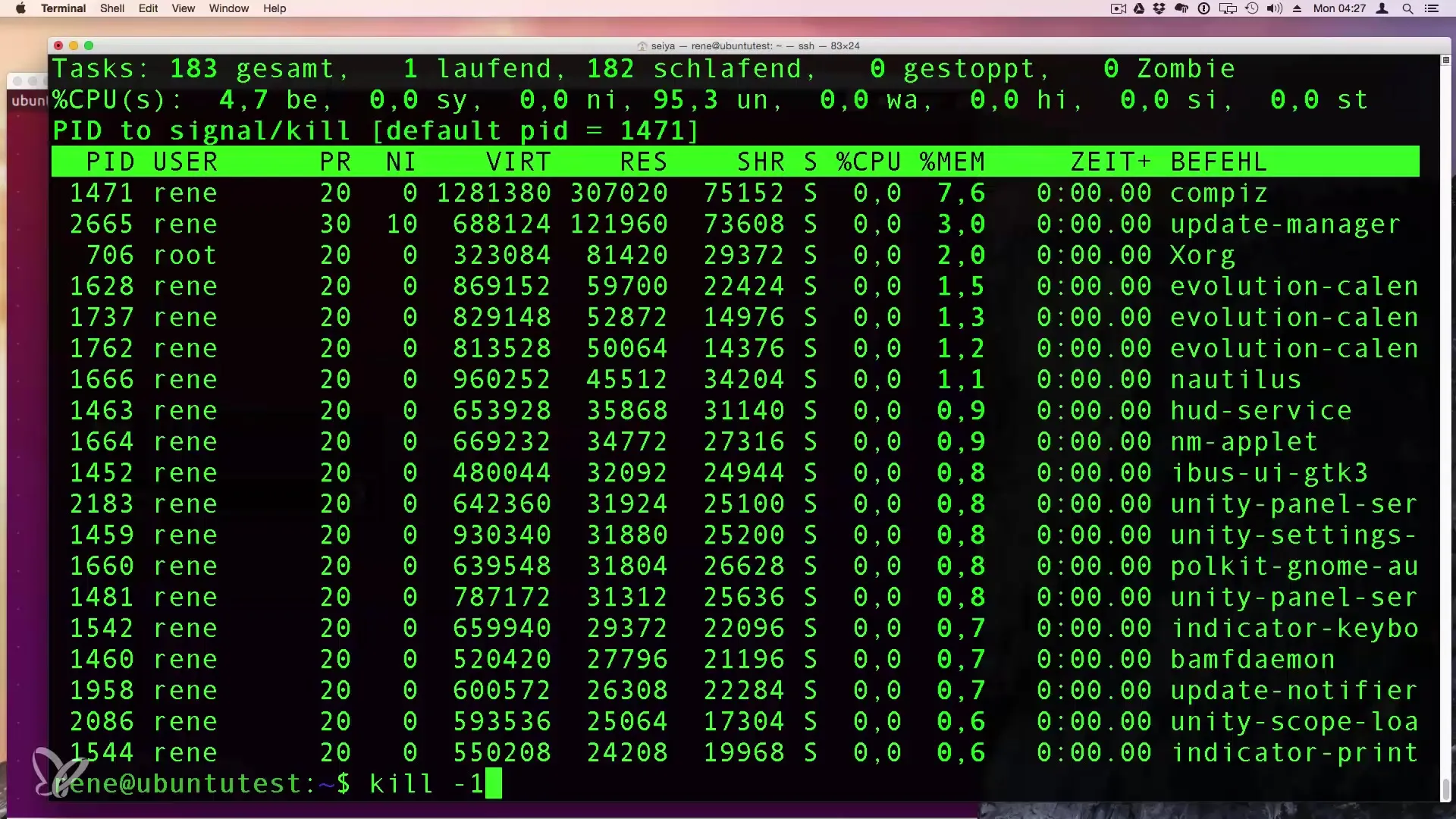
Alternatively, you can use killall -9
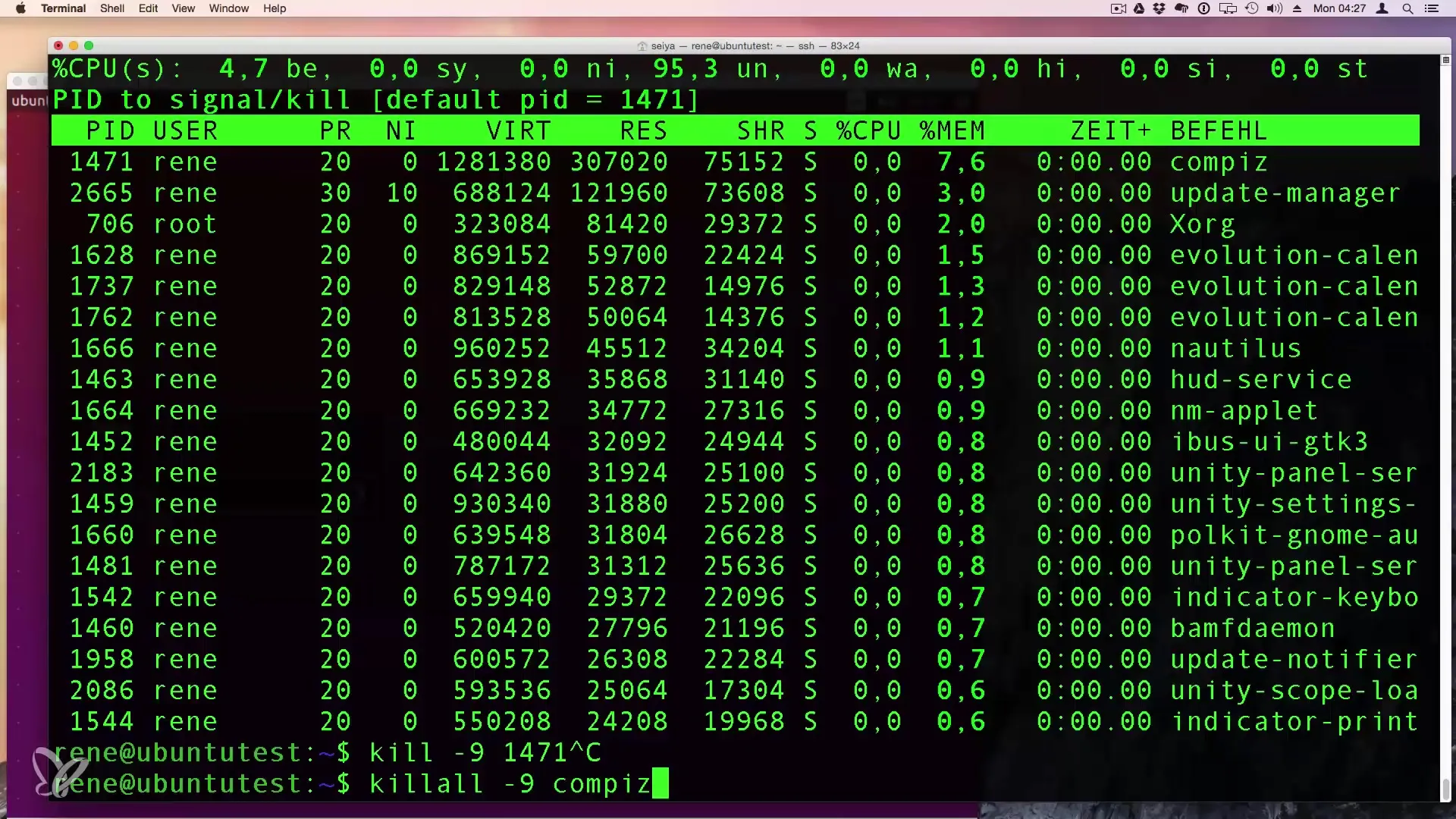
Summary - Effectively Display and Control Processes and Instances in Linux
In this guide, you have learned how to take control of the processes on your Linux system using the commands ps, top, and kill. These tools allow you to monitor the running processes as well as quickly terminate inefficient or unresponsive programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What steps do I need to take to view processes in Linux?Use the command ps for a list of processes running under your user or ps -ax for all processes.
How can I find a specific process?Use the command ps -ax | grep to filter for a specific process.
What does the top command do?top gives you a dynamic overview of all running processes and their resource usage.
How do I terminate a process with kill?Use kill -9 to terminate a process immediately.
Can I terminate multiple processes at once?Yes, with killall -9 you can terminate all instances of a specific program.


