If you are working on web development with PHP, it is beneficial to understand how Sessions work. Sessions allow you to store user information across different page requests. In today's tutorial, you will learn how to read the stored messages from the session for a failed login attempt and display them to the user. We will go through the code step by step and explain all relevant parts.
Key Insights
- Sessions are essential for user identification.
- You can store and retrieve error messages in sessions.
- Messages are displayed conditionally based on the presence of certain session values.
Step-by-Step Guide
To read values from a session that were stored during a failed login, we follow these steps:
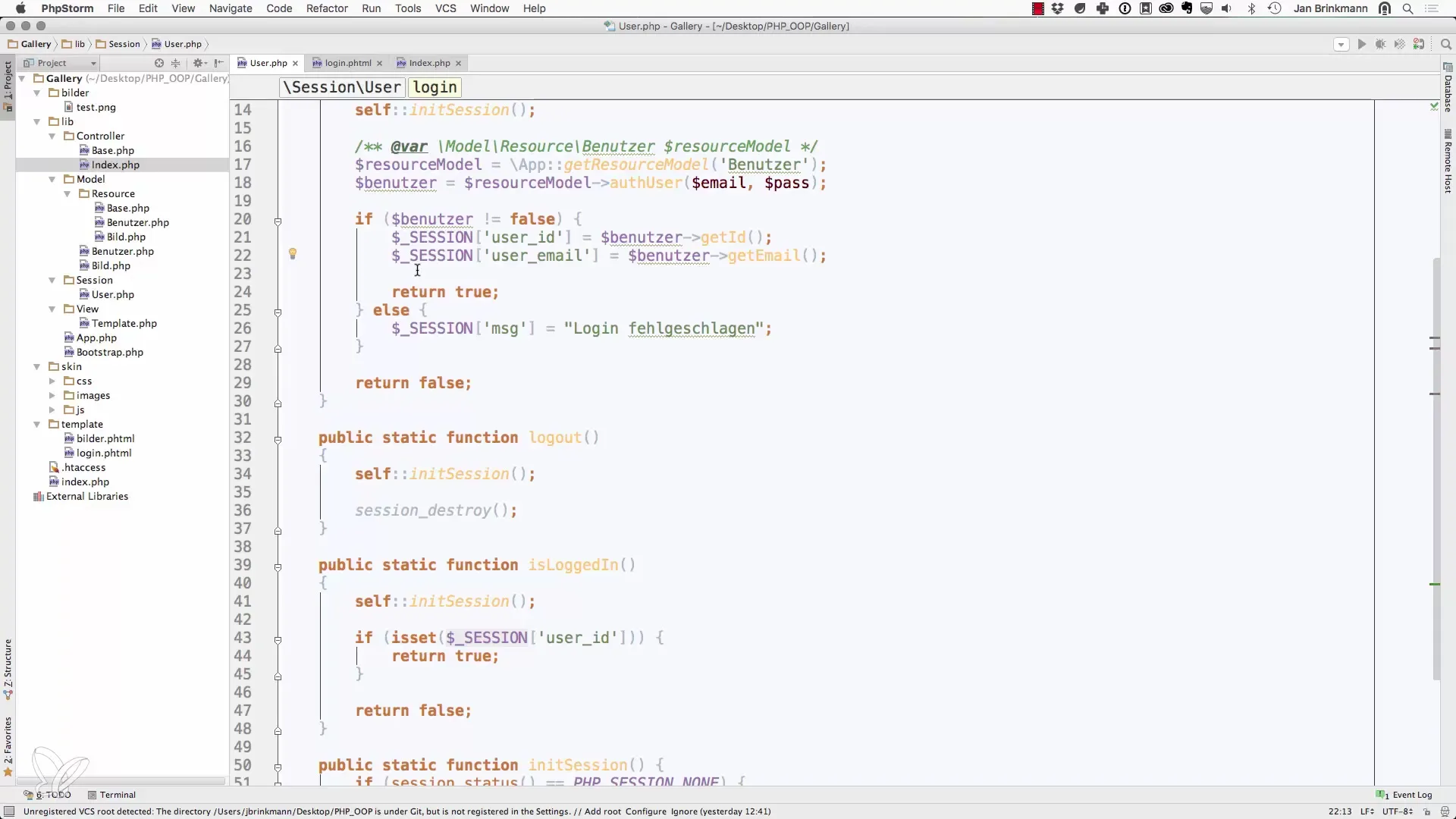
1. Start the session
First, you need to ensure that a session is started for every script execution that uses sessions. This is usually done at the very top of the script. Place the following code at the beginning of your PHP file:
2. Store error message
When a user cannot log in successfully, it is important to notify them. In our case, we store the error message in the session.
3. Check the session variable
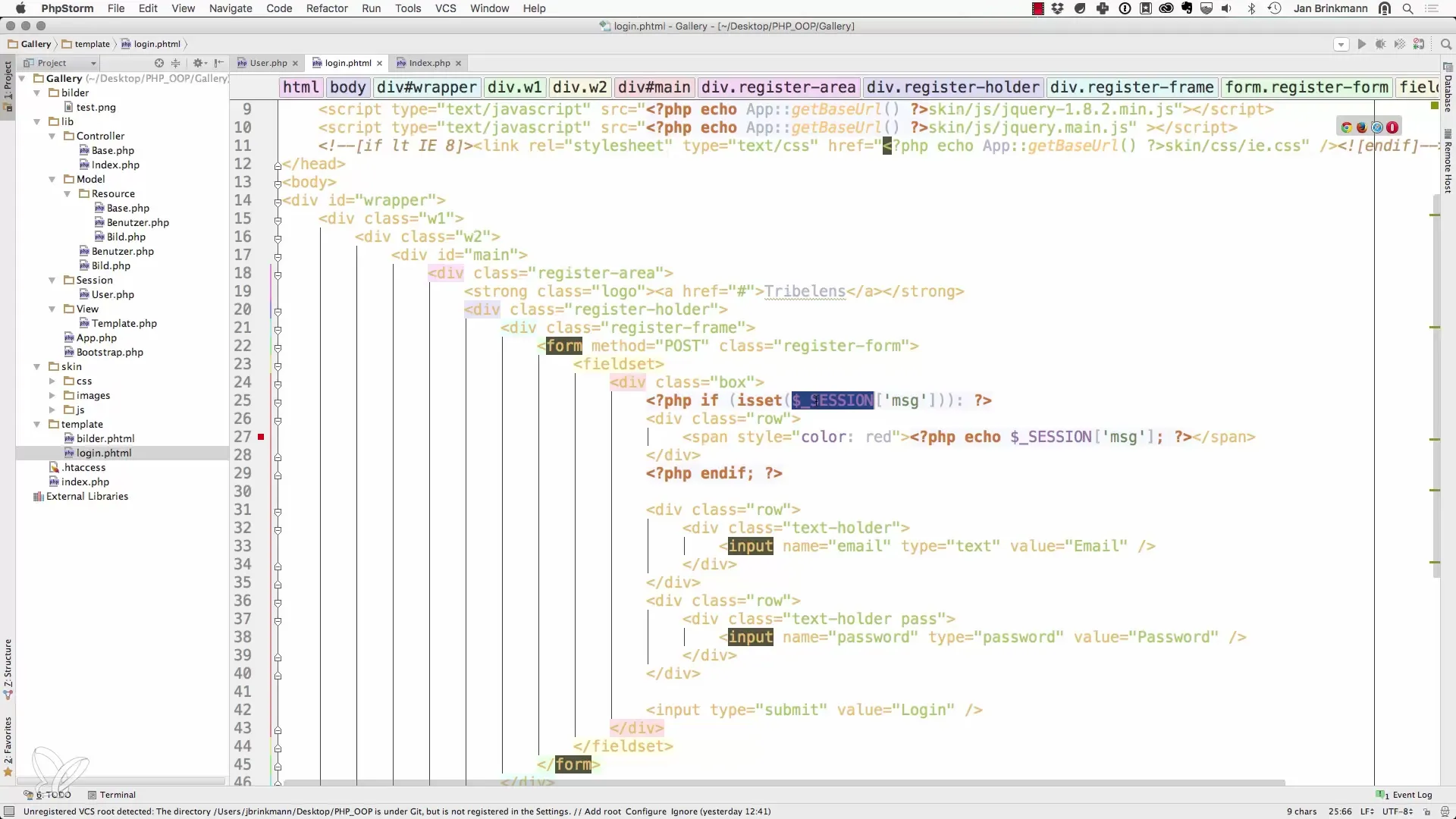
Now we come to the step where we check and display the message from the session. It is important that we perform this check only if the message is indeed set. This is done with isset().
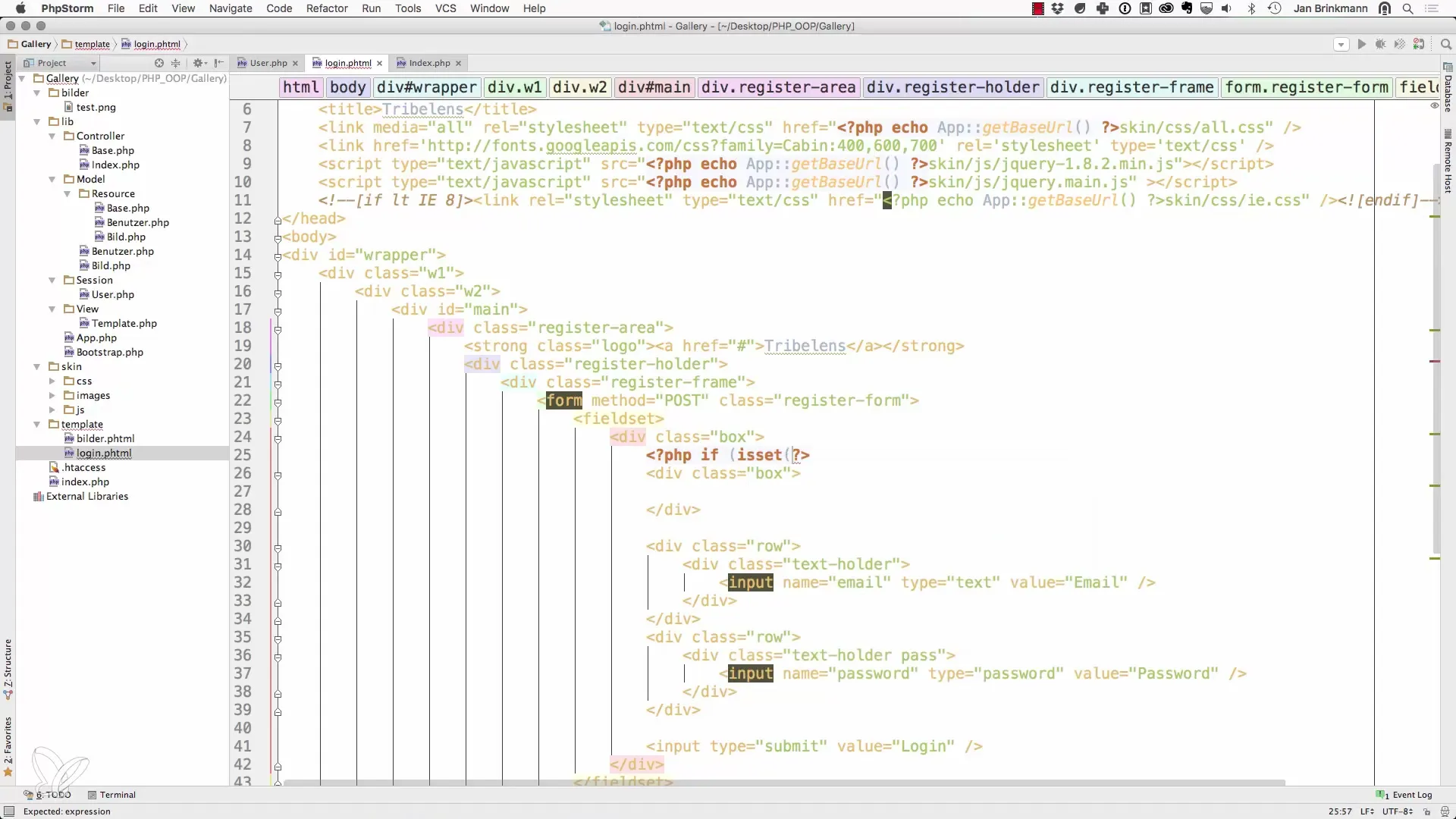
4. Output message on the page
If the message is set, we have the option to display it to the user on the login page. You can create an HTML block that shows the message. For example:
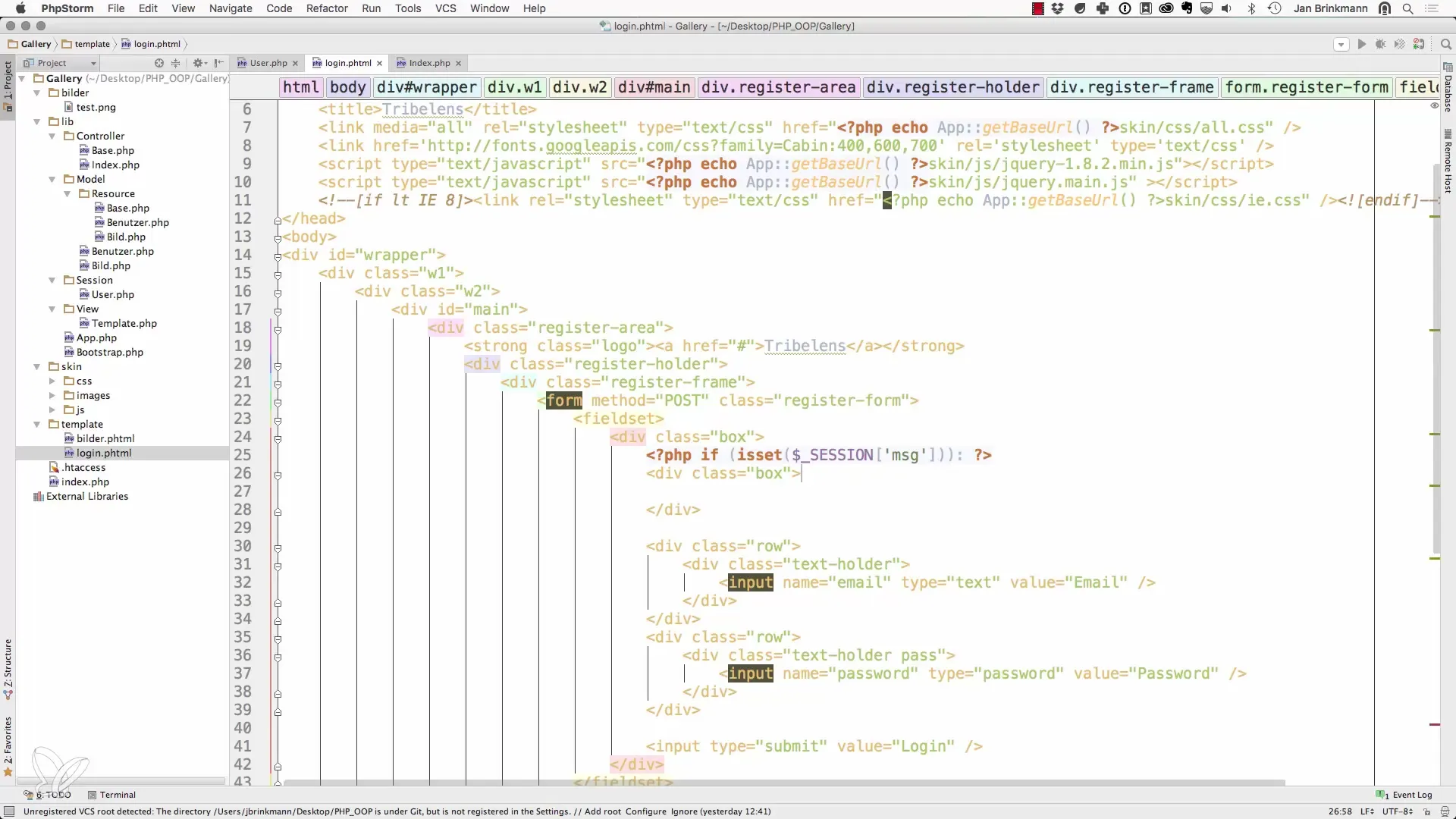
5. Reset session variable after display
It is a good practice to reset the session variable after the message has been displayed to prevent the message from appearing again on a page reload.
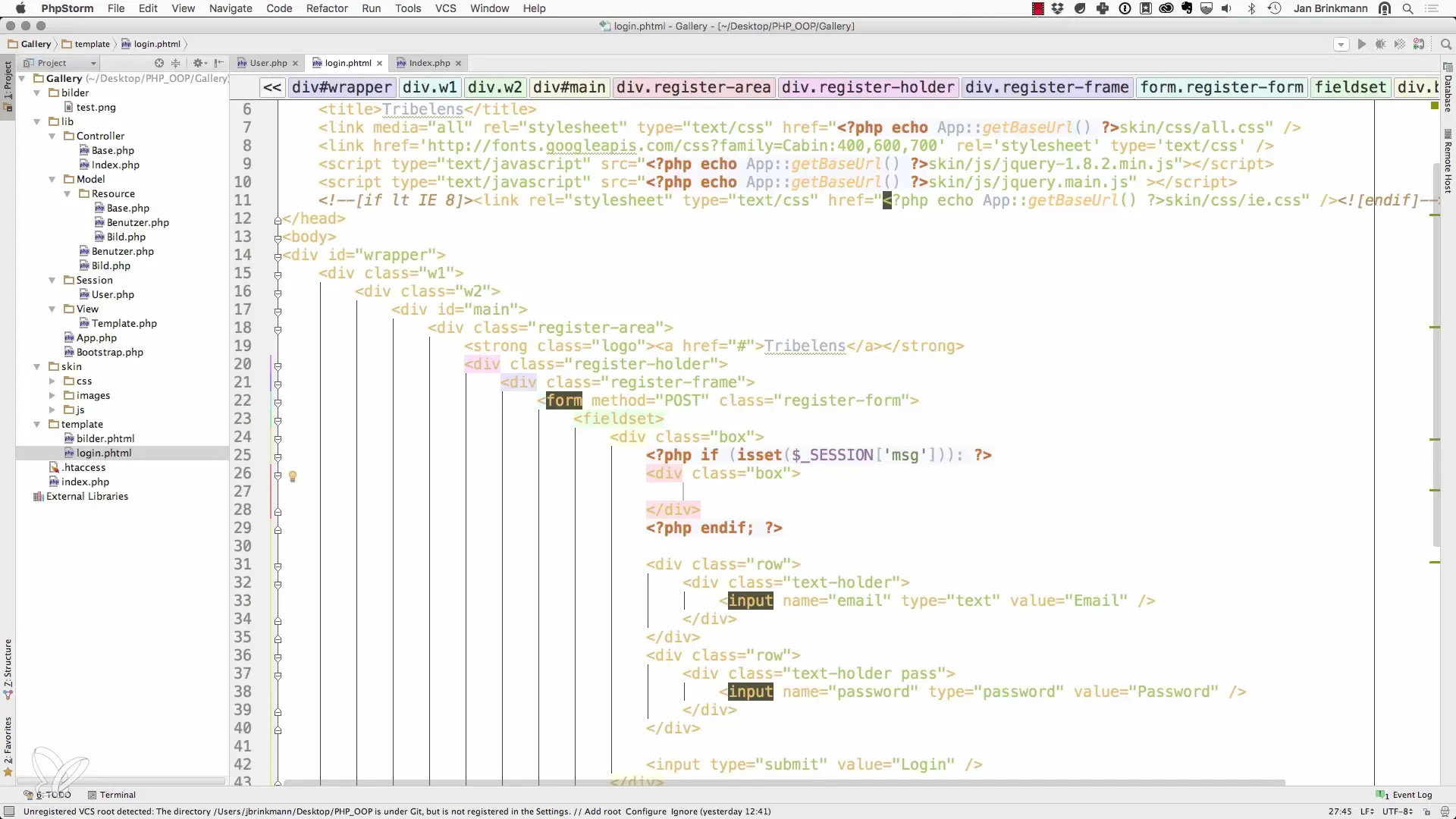
6. Verify and test
Once the above steps have been implemented, it is time to test the functionality. You can do this by intentionally entering incorrect login credentials and checking whether the corresponding error message is displayed.
7. Improve the user interface
If you want to optimize the user interface, you can add additional styles or structure to highlight the error messages and enhance the user experience. Ensure that the input fields are still displayed correctly, and test again to see if everything works as intended.
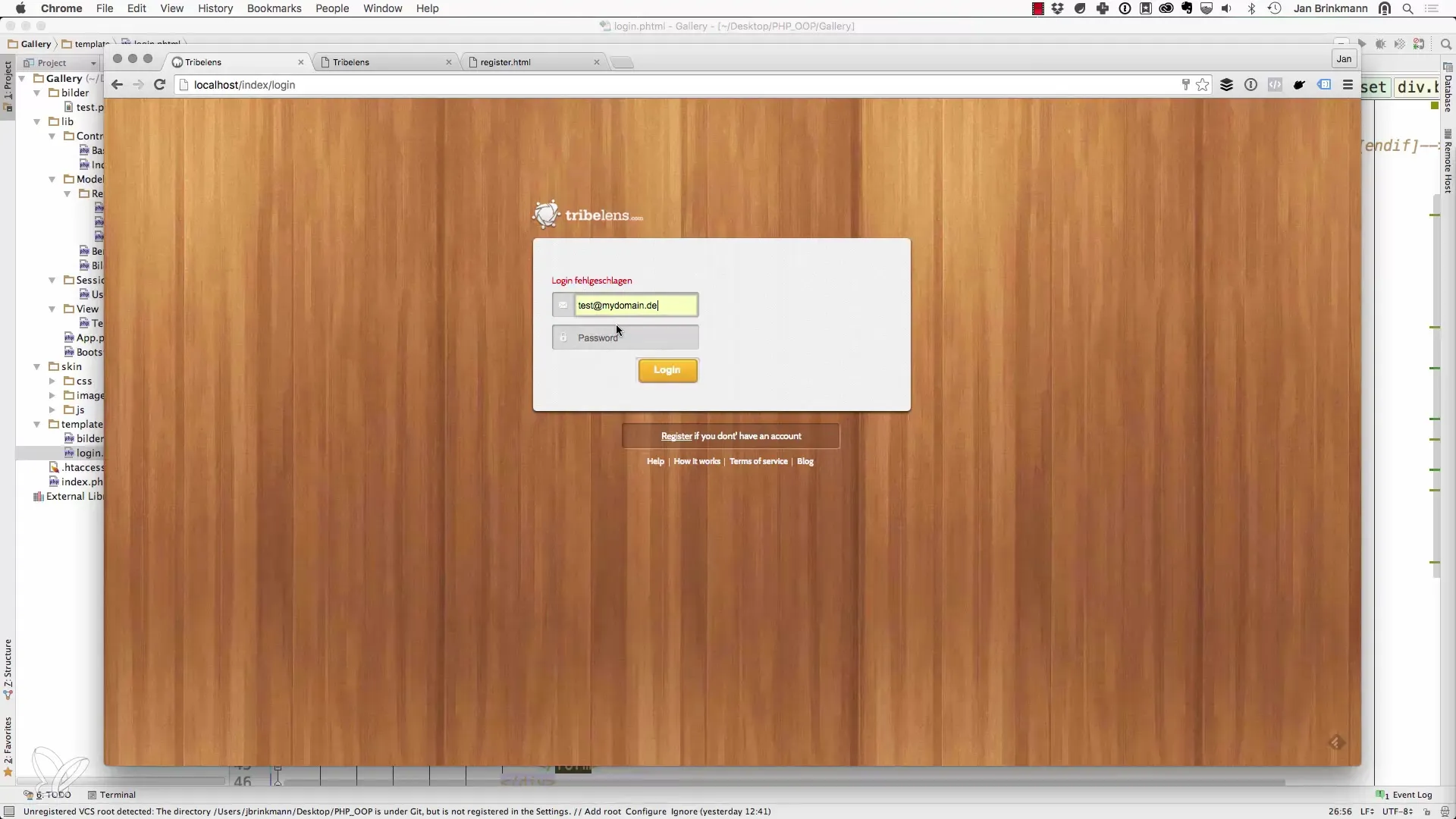
8. Successful login message
If the login is ultimately successful, you can also write a positive message to the session that greets the user. Make sure to apply the same principles for displaying messages that we discussed earlier.
Summary – Displaying values from the session on failed login
In this guide, you learned how to read values from a session to provide feedback to users during a failed login. By utilizing sessions effectively, you ensure a better user experience and provide important information.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are sessions in PHP?Sessions in PHP are a way to store user data across different page requests.
How do I start a session?A session is started in PHP by calling session_start() at the beginning of the script.
How do I read a session variable?You can read a session variable with $_SESSION['variable_name'] after the session has been started.
What should I do after displaying an error message?It is advisable to reset the session variable containing the error message with unset() to avoid repeated displays.
How can I improve the user interface for error messages?You can use CSS to visually highlight error messages and ensure input fields are displayed correctly.


