If you are dealing with graphic design or digital work, you will inevitably encounter various color models. RGBand CMYKare two of the most commonly used color models, and understanding them is crucial for the quality of your designs. This guide highlights the differences between these two models and explains how to effectively use them in AffinityDesigner.
Main Insights
- RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue, while CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black).
- RGB is primarily used for digital applications, while CMYK is used for printing.
- The color representation differs significantly between the two models; RGB colors are more vibrant and vivid.
Understanding Color Models: From RGB to CMYK
To understandthe difference between RGB and CMYK, it is important to know how these color models work. RGB is an additive color model based on light, while CMYK is a subtractive color model used with ink on paper.
RGB is created by adding light in three primary colors: Red, Green, and Blue. These colors are mixed to produce a variety of shades. When all three colors shine at full intensity, white is produced. This model is commonly used for screens and digital media since screens emit light.
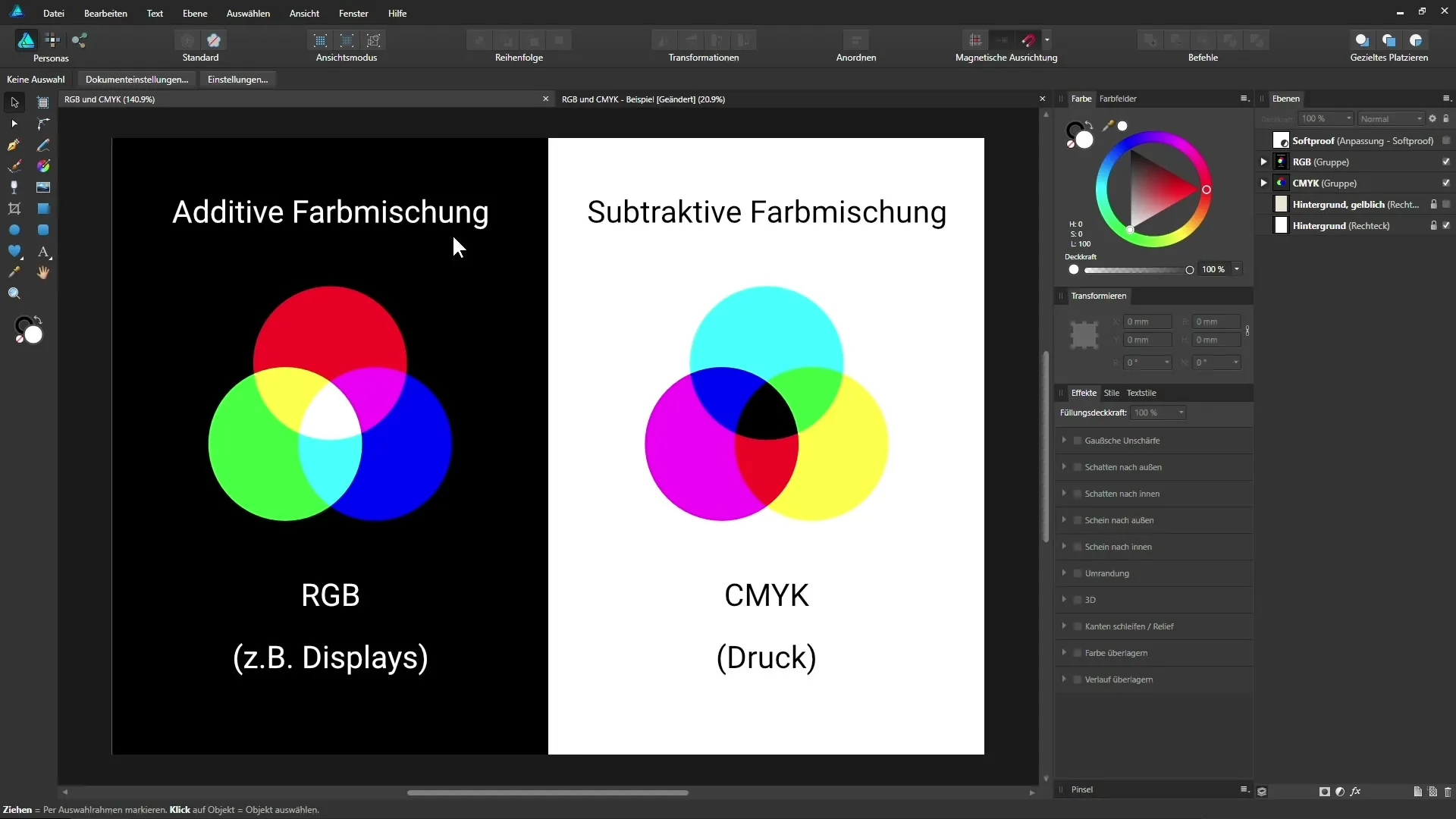
In contrast, the CMYK model uses the colors Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black (Key). Here, color components are subtracted, meaning that by mixing the colors, darker tones are achieved. The tones that appear black from a combination of the other three colors are often not pure black, which is why additional black has been added.
How to Change the Color Format in Affinity Designer
To set the color format for your project in Affinity Designer, open the program and select “File” and then “New”. Here you can choose the desired color formats from RGB to CMYK.
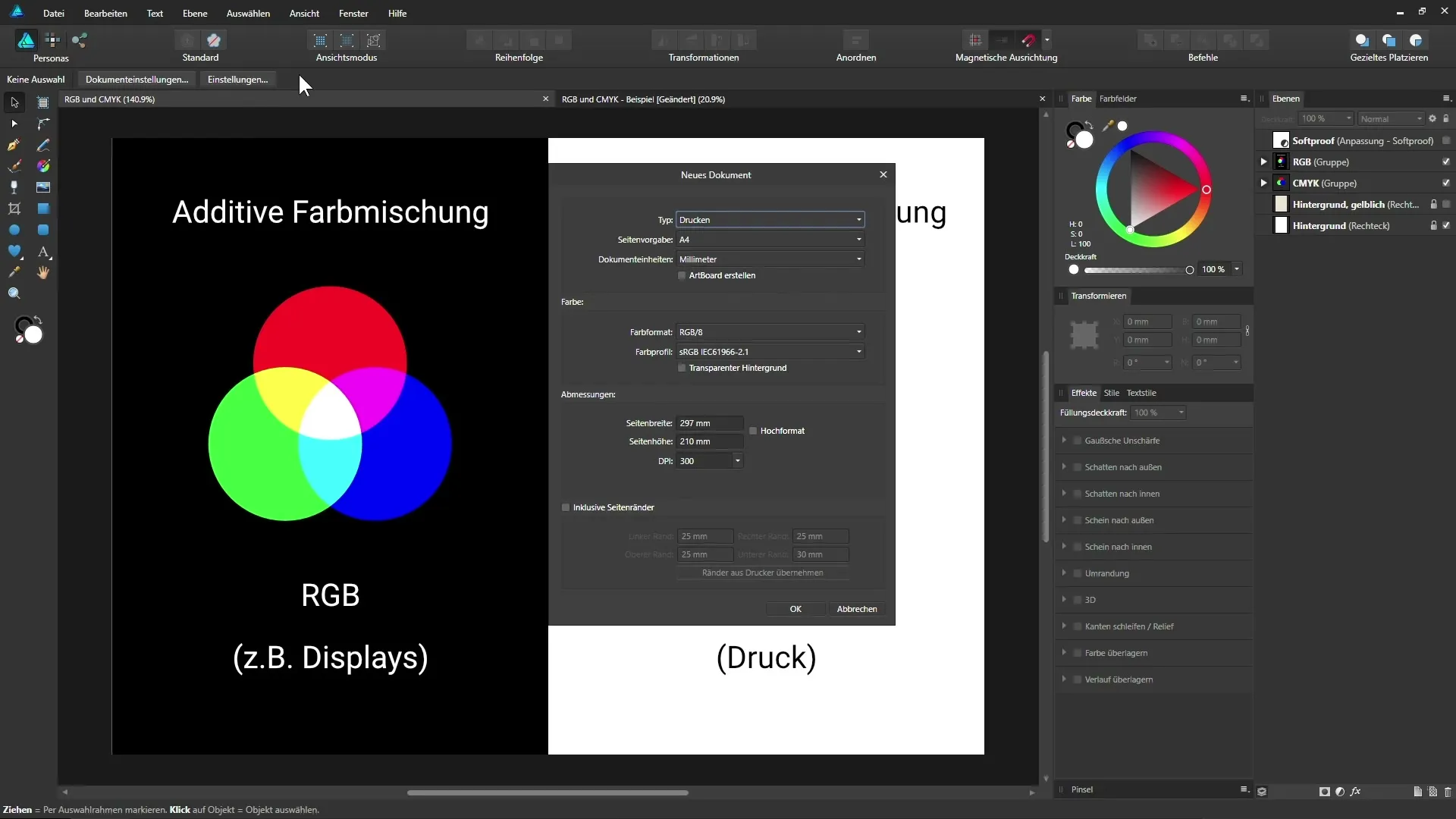
If you have an already opened document, you can change the color settings by clicking on “File” and then “Document Settings.” Here you will see the color format being used and the currently active color profile.
Choosing the right color format is crucial for the type of work you do. RGB is great for digital works since the colors in this format often appear more vibrant and brighter.
The Influence of Paper on the CMYK Color Format
When working in CMYK, the printing process is heavily influenced by the color of the paper. For example, if you have white paper, the colors will appear differently compared to cream or colored paper. Therefore, it is important to plan with the paper color in mind and also use soft proofing to see how your colors will look when printed.
To achieve a realistic simulation of your print in Affinity Designer, you can use a adjustment layer for soft proofing. It allows you to see how the colors might look on paper.
The Importance of Color Management and Calibration
To get the most out of your designs, you should also engage with color management and calibrating your monitor. A calibrated monitor ensures that the colors you see truly correspond to the colors that will be printed. This is especially important when preparing your design for print.
Keep in mind that color representation can vary significantly. If you are mentally working in RGB and the final product is intended for print, you may be disappointed with the print results, as the vibrant colors do not remain the same.
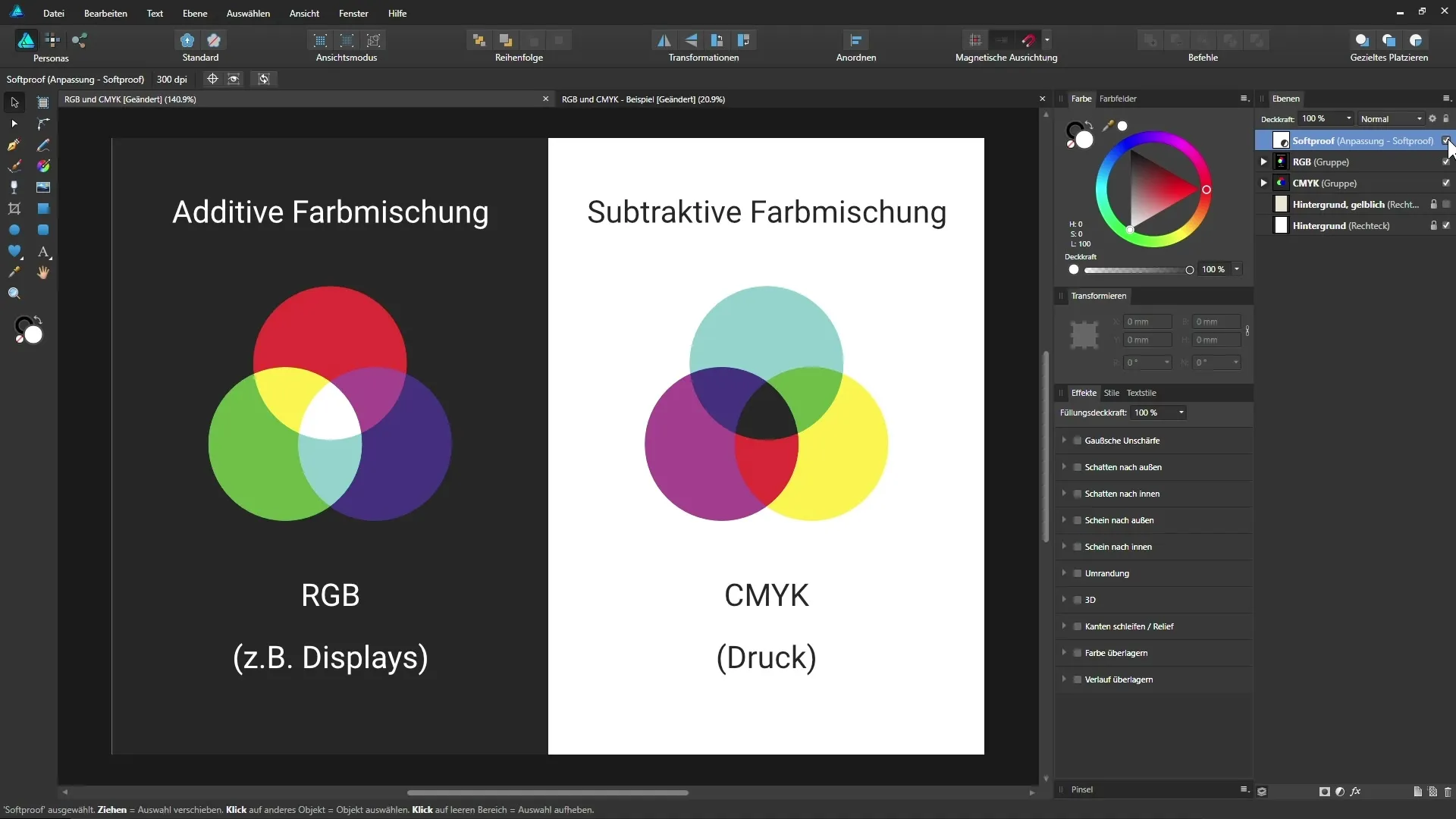
Summary – RGB and CMYK in Affinity Designer: Differences and Applications
Choosing the right color model is one of the crucial decisions you need to make as a designer. RGB is suitable for digital applications, while CMYK is the preferred format for print productions. By understanding these differences, you can ensure that your designs perform optimally both digitally and in print.
FAQ
How do I choose between RGB and CMYK for my project?Select RGB for digital designs and CMYK for print projects.
What impact does the paper have on color representation in the CMYK model?The paper greatly influences color representation; different paper colors can alter the printed colors.
What is soft proofing in Affinity Designer?Soft proofing simulates how a design will look when printed by displaying the results on a monitor.
Do I need a calibrated monitor for design?Yes, a calibrated monitor helps ensure color accuracy between the digital design and the printed product.
Can I work with RGB in Affinity Designer if I am designing for print?It is better to work in CMYK from the beginning to avoid disappointment in printing.


