Multidimensional arrays are an essential concept in programming that frequently appears in various application areas. They allow for storing arrays within arrays, significantly simplifying the structuring and management of data, especially when it comes to complex data structures. In this article, you will learn through a concrete example how to implement and use multidimensional arrays in Java.
Key Insights
- Multidimensional arrays are arrays of arrays.
- The syntax for declaration is similar to that of one-dimensional arrays but requires additional square brackets.
- With multidimensional arrays, you can effectively organize structured data like a calendar.
Step 1: Creating a Two-Dimensional Array
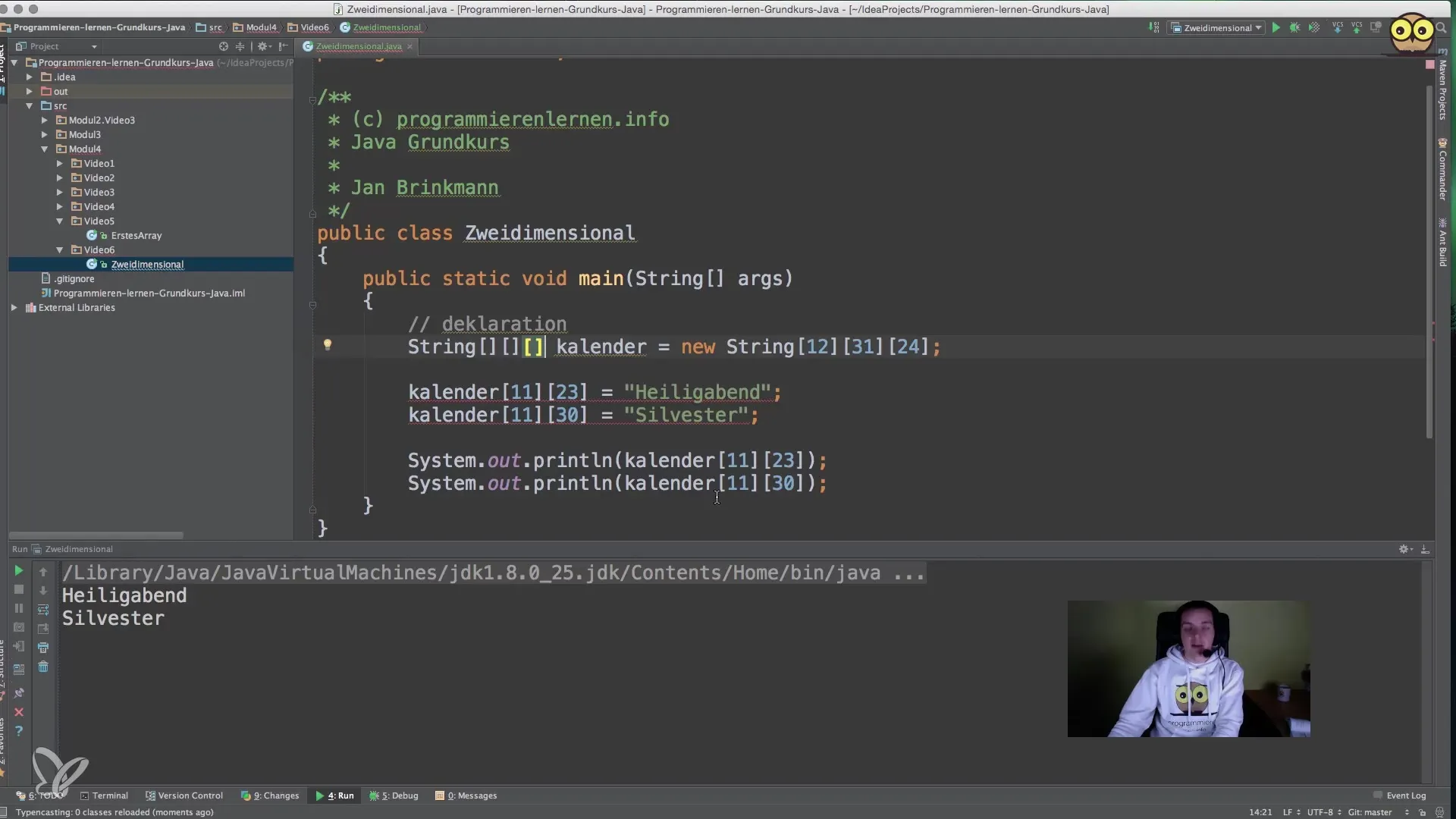
First, you set up a new project in your Java environment. In this example, we will use a two-dimensional array to represent a calendar that includes months and days.
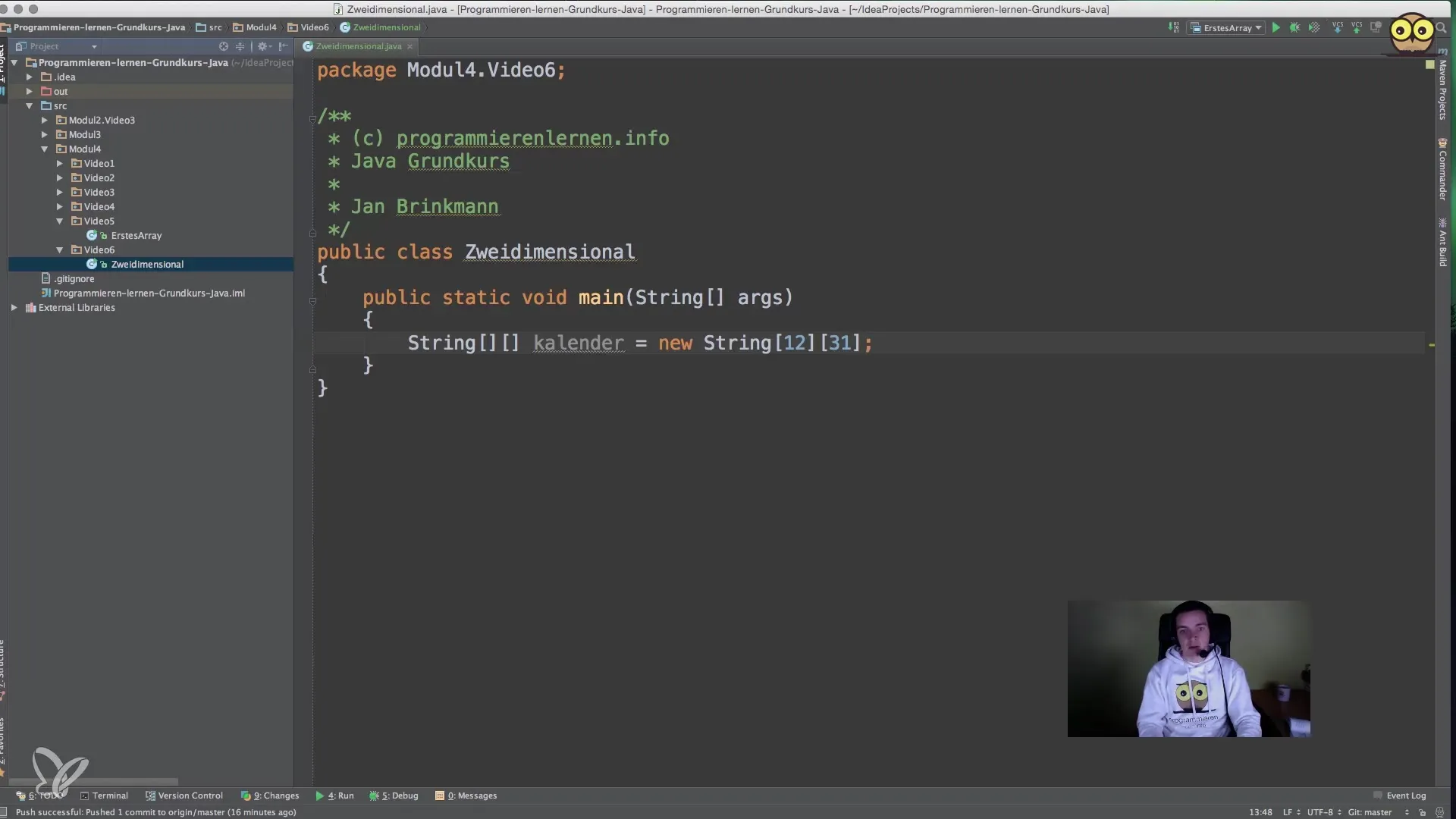
You start by declaring a string array. It will be necessary to define two dimensions using two pairs of square brackets.
Here the array calendar is initialized and created with 12 months and 31 days each. This allows us to store a total of 372 slots, even though not every month has 31 days.
Step 2: Assigning Values
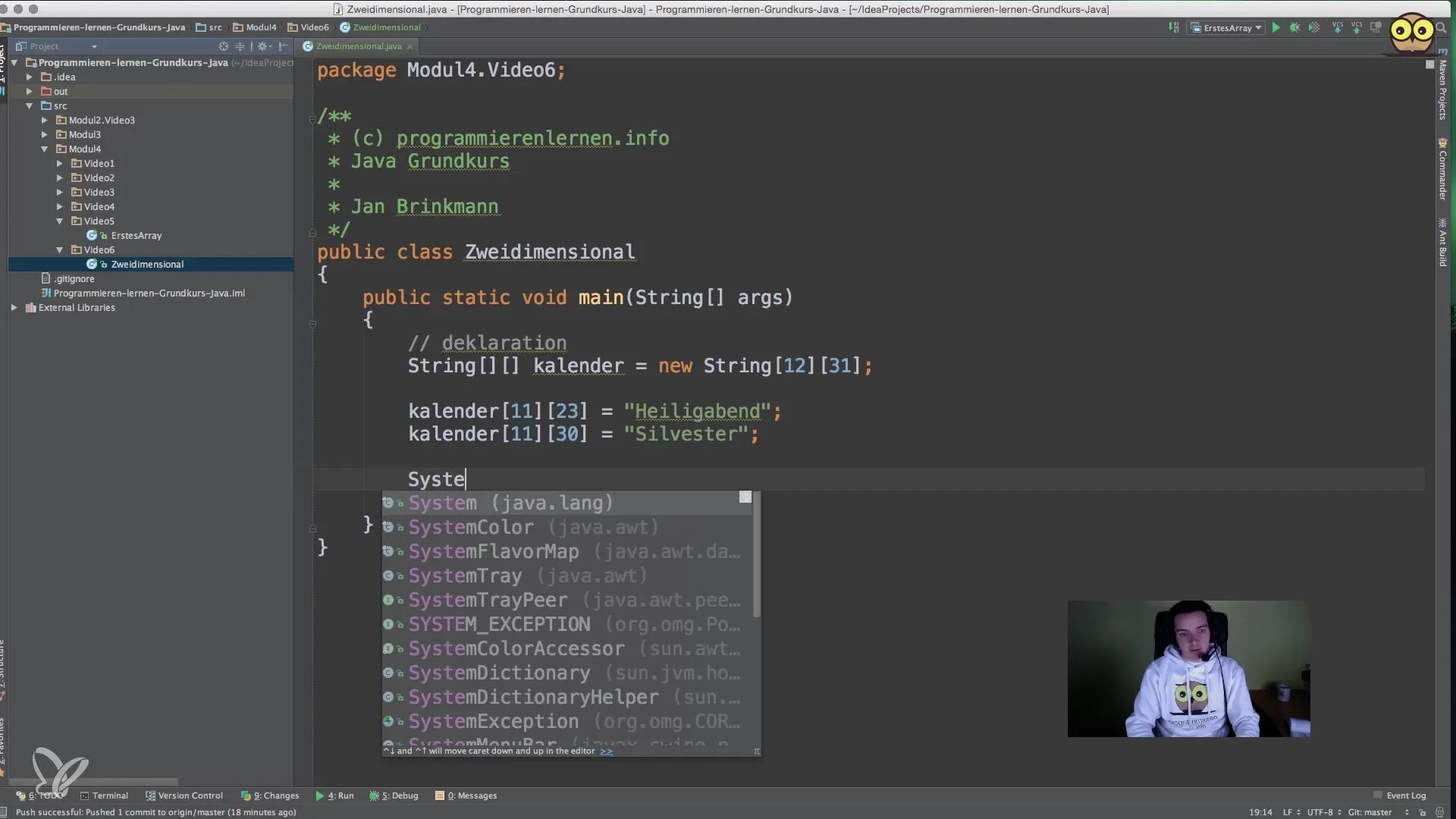
After you have declared the array, the next step is to assign some values. In our example, we want to include relevant holidays in the array to demonstrate how accessing works.
For example, you could add the entry for Christmas Eve on December 24 as a value in the calendar array. You access December first using index 11 and then access the 24th day, which corresponds to index 23.
Example Entries
For December 31, you would proceed similarly. You access the element with indices 11 and 30. Here you can set the entry for New Year's Eve to illustrate how easy it is to access multidimensional data.
Step 3: Outputting Values
To display the stored values, you use System.out.println() to output the holidays to the console. You access the data in the array through the same indices to print the results.
In the case of Christmas Eve, you would use calendar[11][23].
After running your program, you should be able to see the confirmed outputs directly in the console window.
Step 4: Expansion and Complexity
Once you are familiar with the basics of two-dimensional arrays, you can easily add more dimensions. For example, you could store the hours of a day to create a three-dimensional array. This would make the structure even more complex, but it is also easily implementable.
Note that with a variety of dimensions, the clarity diminishes and the imagination is required. While a three-dimensional structure (length, width, height) is still relatively understandable, it can become challenging with four or more dimensions.
Summary
You have now developed a basic understanding of multidimensional arrays in Java. By understanding the principles and working with practical examples, you can create more complex data structures and work with them efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I declare a multidimensional array in Java?You use the syntax: DataType[][] arrayName = new DataType[numberDimension1][numberDimension2];.
How do I access a value in a multidimensional array?You use the index in the form: arrayName[firstDimension][secondDimension];.
Can I also use a multidimensional array for other data types?Yes, you can use multidimensional arrays for any data type such as int, double, or String.
Can I have more than three dimensions in an array?Yes, it is possible to create multidimensional arrays with any number of dimensions, but the complexity of management increases.


